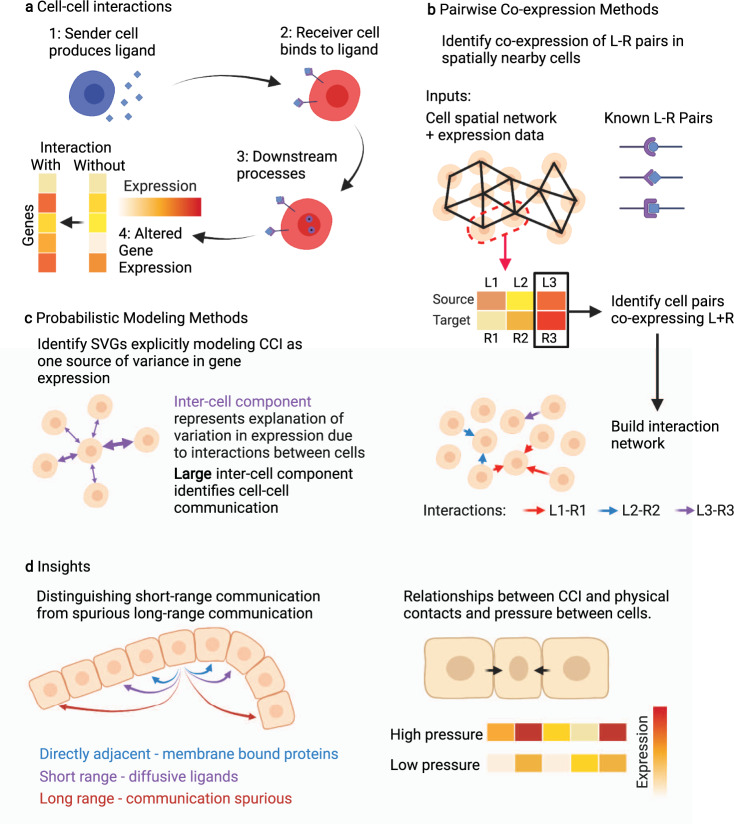
Fig. 3. Illustration of techniques in extracting cell-cell interactions from ST data.
a Cell-cell interactions occur when transfer of a ligand from a sender cell to a receiver cell triggers a downstream response, ultimately leading to changes in gene expression in the receiver cell. b Common techniques identify co-expression of known L-R pairs in cells adjacent in a spatial proximity network, and use this to mark interactions between cells. c Alternatively, some methods probabilistically capture different sources explaining variance in spatial gene expression, including terms capturing intra- and inter-cellular effects. When inter-cellular effects dominate a particular gene’s expression, it is indicative of cell-cell interaction. d Insights made from CCI analysis of spatial data include the ability to determine interactions of a particular cell by filtering out spurious long-range connections, and investigations into the relationship between L-R interactions, and mechanistic interactions and cell proximity.