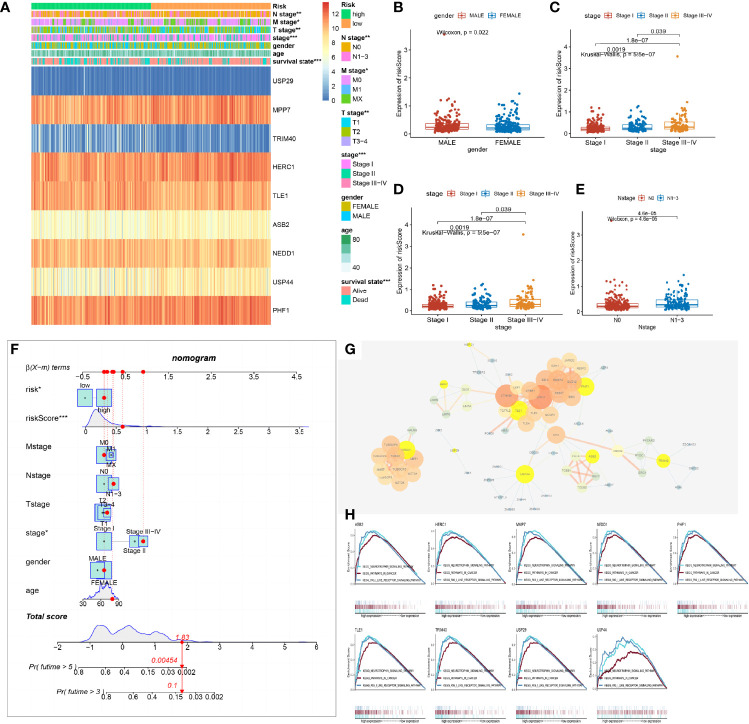
Figure 4.
Relationship between the prognostic risk model and the clinical indexes. (A) Heat map of the model’s stratification, clinical indexes, and gene prognostic model. (B–E) Box plot showing the difference between high- and low-risk groups about gender, stage, N stage, and T stage. P-values were calculated with the Wilcoxon test. (F) Nomogram model of the risk score and other clinical factors to predict the progression of lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD). (G) Protein and protein network interaction of 9 model genes. Yellow color represents the 9 model genes. The size of the circle and the thickness of the line represent the combined score. (H) Gene Set Enrichment Analysis of a single gene of the 9 model genes associated with the low and high expression of LUAD of The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and demonstrated in the three commonly participating pathways, including neurotrophic, cancer, and Rig I-like receptor signaling pathways.