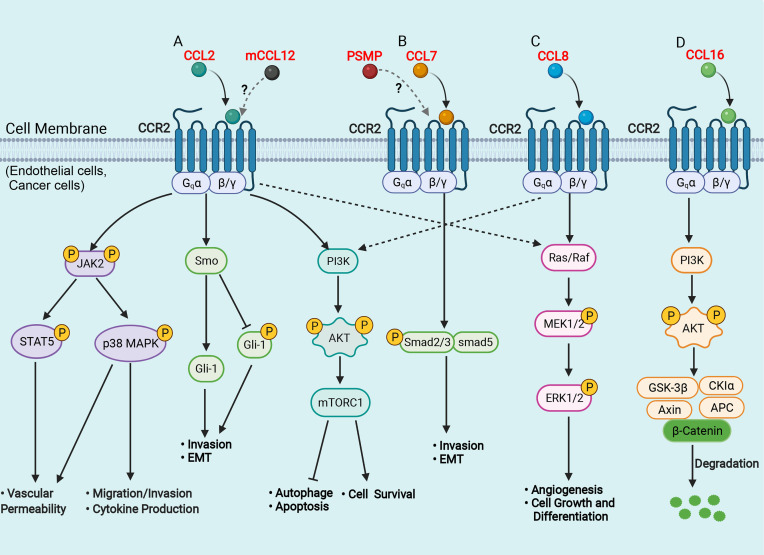
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of signaling pathways in the liver of CCR2 and its ligands. (A) CCL2 binds to CCR2 and activates JAK2, triggering several downstream pathways, such as STAT5 and p38MAPK, which enhance vascular permeability, promote cell migration and invasion, favor cytokine production; CCL2 binds to CCR2 and activates the Hh signaling pathway, and increases the expression of Smo and Gli-1, which induce cell invasion and EMT; CCL2 binds to CCR2 and activates the PI3K/Akt/mTORC1 pathway, promoting cell survival and inhibiting autophagosome formation and cell apoptosis. (B) CCL7 binds to CCR2 and activates the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway, which promotes cell invasion and EMT; (C) CCL8 binds to CCR2 and activates the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway, enhancing cell growth and differentiation and promoting angiogenesis. (D) CCL16 binds to CCR2 and activates PI3K/AKT/GSK3β signaling, which results in GSK3β proteasomal degradation and enhances β-catenin stability. AKT, protein kinase B; APC, adenomatous polyposis coli; CK1, casein kinase 1; EMT, epithelial-mesenchymal transition; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; Hh, hedgehog; Gli, glioblastoma; GSK3β, glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta; JAK2, Janus kinase 2; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; MEK, mitogenic effector kinase; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; Smo, smoothened; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription protein. (Figure created with BioRender.com).