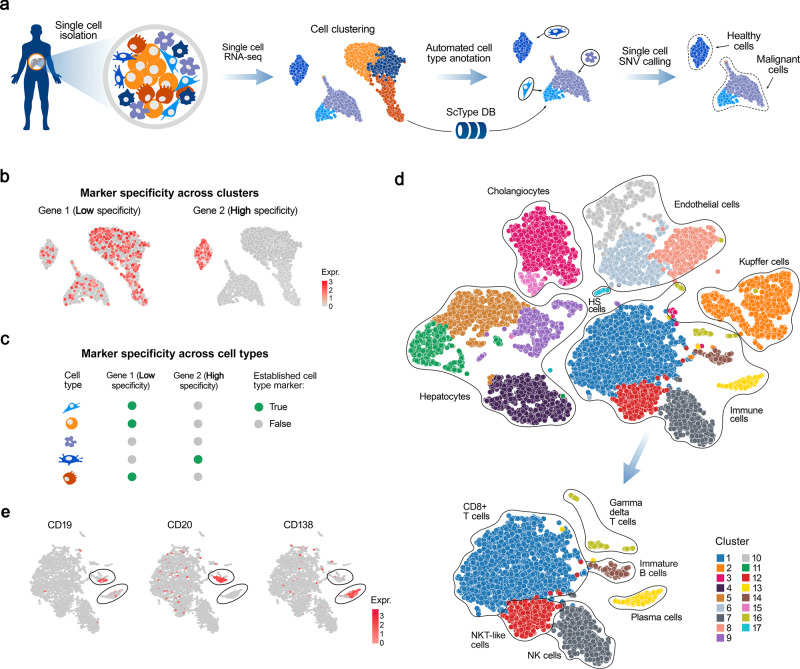
Fig. 1. A schematic view of cell-type annotation using ScType.
a ScType requires only the raw or pre-processed single-cell transcriptomics dataset(s) as input. ScType implements options for additional quality control and normalization steps, where needed, followed by unsupervised clustering of cells based on scRNA-seq profiles. The results here are based on the Louvain clustering; however, also SC3, DBSCAN, GiniClust and k-means clustering options are available in ScType (see Methods). In the next step, ScType performs a fully-automated cell-type annotation using an in-built comprehensive marker database. Finally, ScType implements novel options for somatic single-cell SNV calling to distinguish between healthy and malignant cell populations. b, c ScType specificity score guarantees that the marker genes show specificity both across clusters and cell types for accurate unsupervised cell-type annotation with high cell subpopulation selectivity. d UMAP example of automated cell subtype identification by ScType in the liver atlas dataset, where it automatically labelled the same cell-types as assigned manually in the original study10. e Based on the information that plasma cells do not express common B-cell markers, such as CD19 and CD20, but instead express CD138, ScType enhanced the resolution of cell-type annotations of two cell clusters, which were jointly annotated as B-cells in the original study, by segregating them into immature B-cell and plasma (B) cell types (lower UMAP plot of panel (d).