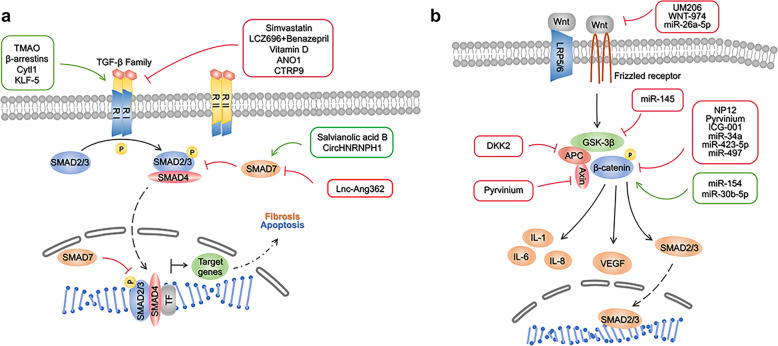
Fig. 6.
a TGF-β/SMADs signaling pathway and targeted therapy in MI. After TGF-β family binds to TGFβRII, TGFβRI is phosphorylated on specific serine and threonine residues, and finally forms a heterocomplex. The receptor complex reacts with the downstream effector molecule SMADs protein and eventually regulates the transcription of the target gene. RI receptors type I, RII receptors type II, TF transcriptional factor, R-Smad receptor-regulated Smad, Co-Smad common Smad, I-Smad inhibitory Smad, TMAO trimethylamine N-oxide, KLF5 Kruppel-like factor 5, Cytl1 cytokine-Like 1, ANO1 Anoctamin-1, CTRP9 C1q/tumor necrosis factor-related protein-9. b Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and targeted therapy in MI. Wnt signaling is considered as a basic growth regulation pathway. The binding of Wnt to the Frizzled receptor family and low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5) or LRP6 co-receptors stimulates the canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, thereby regulating the stability of β-catenin and context-related transcription. Wnt wingless, LRP LDL receptor-related protein, APC adenomatous polyposis coli, GSK-3β glycogen synthase kinase 3β, VEGF vascular endothelial growth factor, SMAD small mother against decapentaplegic, IL interleukin, DKK2 Dickkopf-related protein 2