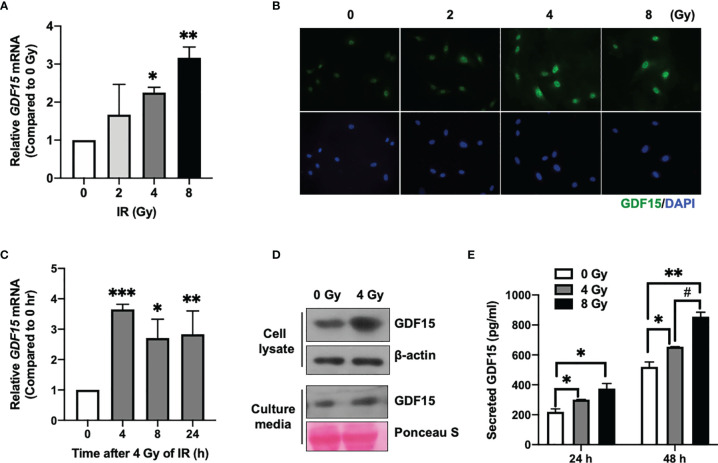
Figure 1.
Effect of ionizing radiation (IR) on GDF15 expression in human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMVECs). (A) Effect of different doses of IR on GDF15 mRNA expression in HBMVECs. Cultured cells were harvested 24 h post-IR exposure, and GDF15 mRNA levels were analyzed using quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). (B) Effect of different doses of IR (0 – 8 Gy) on GDF15 protein levels in HBMVECs. GDF15 protein expression was detected by immunofluorescence analysis using anti-GDF15 antibody (green). Nuclei were stained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (blue) (Magnification: 400×); (C) Time course of GDF15 mRNA expression after irradiation with 4 Gy of IR. GDF15 mRNA levels measured using qRT-PCR at the indicated time points. (D) Immunoblotting analysis of GDF15 in the cell lysate and culture medium reveals that IR upregulated GDF15 protein levels. Cells and culture media were harvested at 24 h post-IR exposure. (E) IR promotes the secretion of GDF15. The secretion of GDF15 into the culture medium was measured using a human GDF15 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit at 24 and 48 h post-irradiation with 4 or 8 Gy of IR. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation of three experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 compared with the control. ## p < 0.05 compared with 4 Gy.