FIGURE 1.
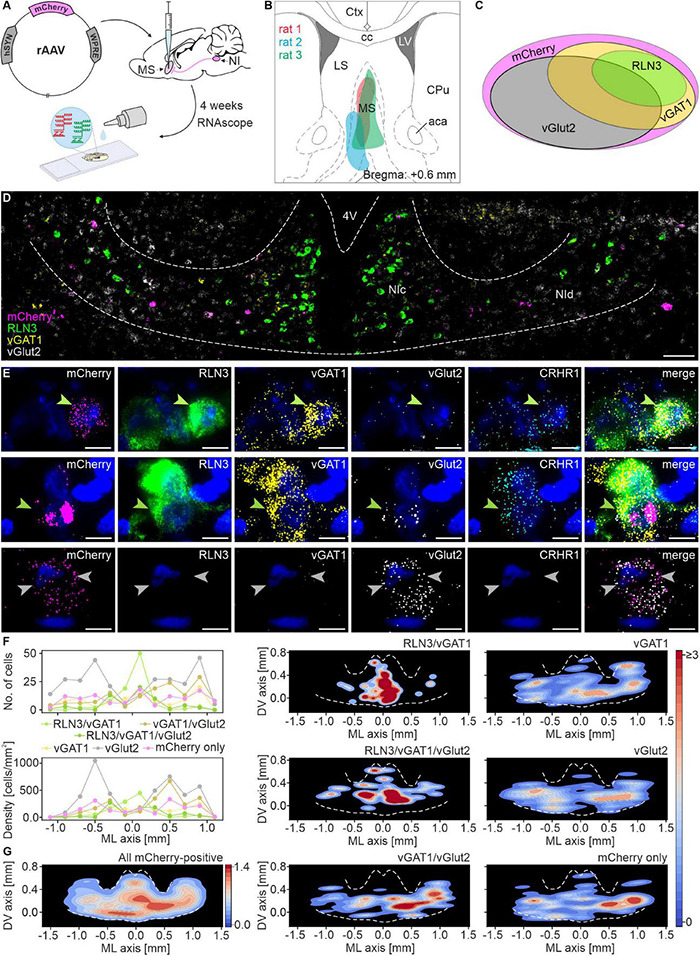
Multiple mRNA species detected in nucleus incertus neurons that directly innervate the medial septum. (A) Experimental procedure. (B) Reconstruction of the sites of retrograde pAAV-hSyn-mCherry viral vector injections in the MS. (C) Schematic of the proportions of and relationship between the distinguished types of MS-innervating NI neurons (area of each ellipse matches the percentage of each specific cell type). (D) Representative image of mCherry (pink), RLN3 (green), vGAT1 (yellow), and vGlut2 (light-gray) mRNA-expressing neurons in NI. Scale bar: 100 μm. (E) A series of images illustrating exemplary MS-innervating NI cells expressing each mRNA examined with DAPI-stained nuclei (blue): top, a RLN3/vGAT1/CRHR1 mRNA-expressing neuron (green arrowhead); middle, a RLN3/vGAT1/vGlut2/CRHR1 mRNA-expressing neuron (green arrowhead); bottom, two vGlut2 mRNA-expressing neurons (light gray arrowheads). Scale bars: 10 μm. (F) Medial-lateral axis distribution of the number (upper panel) and density (lower panel) of MS-innervating NI neurons. Bin size: 200 μm. (G) Density scatter plots with color-coded probability density function of all MS-innervating NI neurons, created for all (left panel) and for each individual type of MS-innervating NI neuron (middle and right panel); dotted white line delineates NI area. 4V, 4th ventricle; NIc, nucleus incertus pars compacta; NId, nucleus incertus pars dissipata; RLN3, relaxin-3; vGAT1, vesicular γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) transporter; vGlut2, vesicular glutamate transporter.
