FIGURE 10.
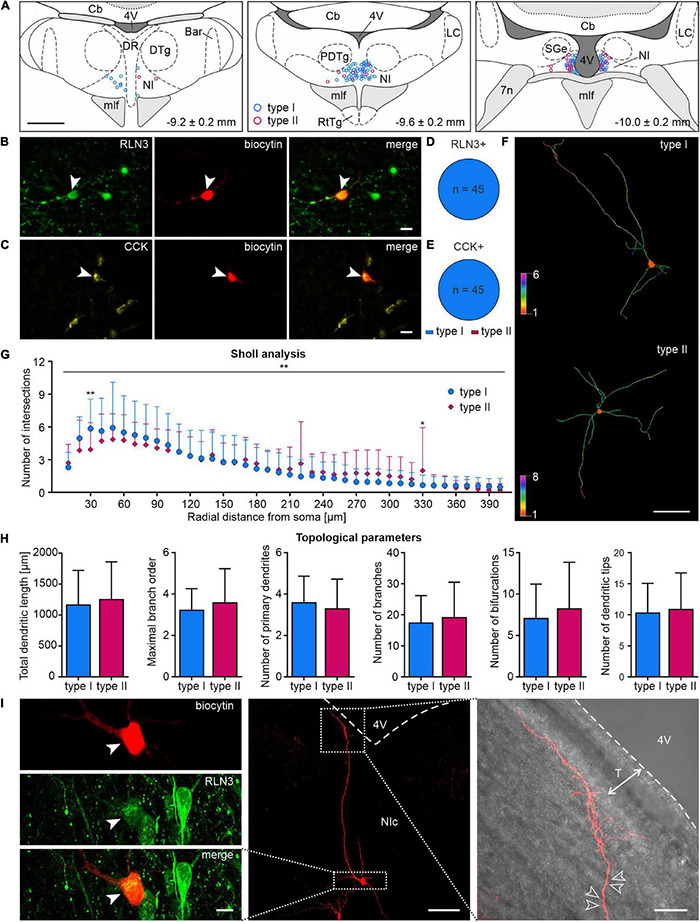
Localization, morphology and neuropeptide content of type I and II NI neurons. (A) Reconstruction (relative to bregma, lower right corner), of the localization of type I (blue circles) and type II (pink circles) NI neurons recorded during patch clamp experiments. (B) Post-recording immunofluorescent identification of NI neurons: image of RLN3+ NI neuron (green, white arrowhead); biocytin (red, white arrowhead) and merge. Scale bar: 20 μm. (C) Image of CCK+ NI neuron (yellow, white arrowhead); biocytin (red, white arrowhead) and merge. Scale bar: 20 μm. (D,E) Electrophysiological types of RLN3+ and CCK+ NI neurons, respectively. (F) 2D view of representative dendritic traces of type I (top) and type II (bottom) neurons, drawn with colors representing the number of dendrites intersecting with Sholl spheres. Scale bar: 100 μm. (G) Sholl analysis and comparison of the dendritic trees of type I and II NI neurons; despite a significant interaction between neuron type and distance from soma, significant differences, indicated by asterisks, were found only at 30 and 330 μm from soma. Significance indicated by two-way RM ANOVA and Uncorrected Fisher’s LSD post-hoc test: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. (H) Topological parameters of type I and II NI neurons (total dendritic length, maximal branch order, number of primary dendrites, branches, bifurcations and dendritic tips). (I) Images of a representative, biocytin-filled NI RLN3+ neuron (left panel, cell body indicated with a white arrowhead), with thin, tuft-like distal dendrites pointing toward the 4th ventricle (right panel; empty arrowheads indicate exemplary dendritic spines; white dotted line with arrows indicates the extent of tanycytes, T). Boxed areas in the middle panel represent the area surrounding the cell body (left panel) and the tuft-like distal dendrites (right panel). 4V, 4th ventricle; Bar, Barrington’s nucleus; Cb, cerebellum; CCK, cholecystokinin; DR, dorsal raphe nucleus; DTg, dorsal tegmental nucleus; mlf, medial longitudinal fasciculus; NI, nucleus incertus; NIc, nucleus incertus pars compacta; RLN3, relaxin-3; RtTg, reticulotegmental nucleus of the pons; T, tanycytes.
