FIGURE 4.
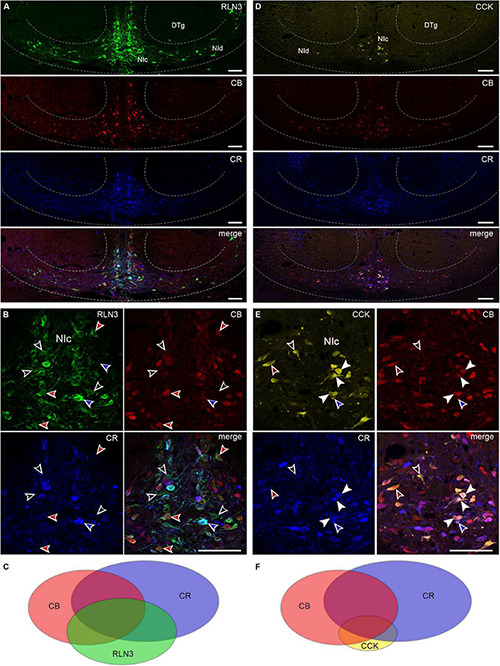
RLN3 and CCK colocalization with calcium-binding proteins in nucleus incertus neurons. (A) Overview of immunofluorescence in the NI region for RLN3 (green), CB (red), CR (blue), and a merged image (bottom); and (B) combinations of colocalization of the tested markers: RLN3-CB neurons devoid of CR (red arrowheads), RLN3-CR neurons devoid of CB (blue arrowheads), RLN3 neurons devoid of CR, and CB (black arrowheads). (C) Schematic of the proportions of and relationships between RLN3 and the tested calcium-binding proteins. (D) Representative images of coronal sections through the NI with immunofluorescence for CCK (yellow), CB (red), and CR (blue), and a merged image illustrating colocalization of the tested markers. (E) Colocalization of CCK with calcium-binding proteins: CCK neurons positive for CB and CR (white arrowheads), CCK neurons positive for only CB (green arrowheads), or CR (blue arrowheads), or neither calcium-binding protein (black arrowheads). (F) Schematic of the relationship between CCK, CB, and CR. Scale bars: 100 μm. CB, calbindin; CCK, cholecystokinin; CR, calretinin; DTg, dorsal tegmental nucleus; NIc, nucleus incertus pars compacta; NId, nucleus incertus pars dissipata; RLN3, relaxin-3.
