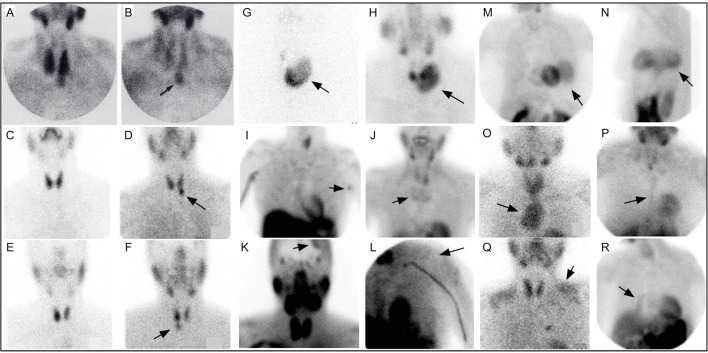
Figure 4.
Early 99mTc-sestamibi parathyroid imaging (A) with uniform uptake within the thyroid and more mild focal uptake in the left lower neck, inferior to the thyroid. (B) Delayed image shows decreased radiotracer uptake within the thyroid and increased radiotracer uptake within a 2.5g parathyroid adenoma (arrow). Example of dual tracer method (C–F) with left image depicting 99mTc-pertechnetate and right image depicting 99mTc-sestamibi showing a left PA (D) and right PA (F). Uptake not related to PA (arrows) can also be seen (G–R). Multinodular goiter 99mTc-pertechnetate (G) and 99mTc-sestamibi (H). Also depicted on 99mTc-sestamibi are (I) left axillary skin fold, (J) manubrium brown tumor, (K) meningioma, (L) deltoid implant, (M) diaphragmatic hernia anterior and (N) lateral, (O) retropharyngeal PA and goiter extending into mediastinum, (P) sternotomy, (Q) muscle uptake, (R) atelectasis adjacent to mediastinum on the right. Reproduced with permission from: Taillefer R, Boucher Y, Potvin C, Lambert R. Detection and localization of parathyroid adenomas in patients with hyperparathyroidism using a single radionuclide imaging procedure with technetium-99m-sestamibi (double-phase study). J Nucl Med. 1992 Oct;33(10):1801-7. PMID: 1328564.