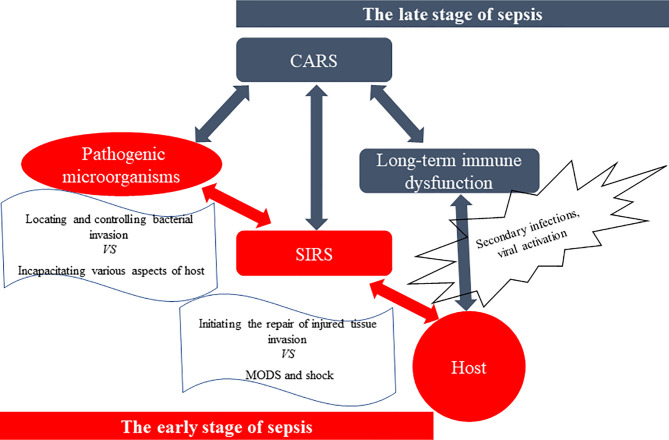
Figure 2.
The antagonism between the host and pathogenic microorganisms. The spread of pathogens, especially Gram-negative bacteria, and their products [such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS), etc.] causes systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), which leads to multiple organ dysfunction syndromes (MODS) and shock, and even death. However, surviving patients suffer from a stage of compensatory anti-inflammatory response syndrome (CARS), especially immunosuppression, and experience a long-term immune dysfunction called immuno-paralysis. And they are more susceptible to secondary infections, increased viral activation, and reduced 5-year survival rate, compared to those who do not have sepsis.