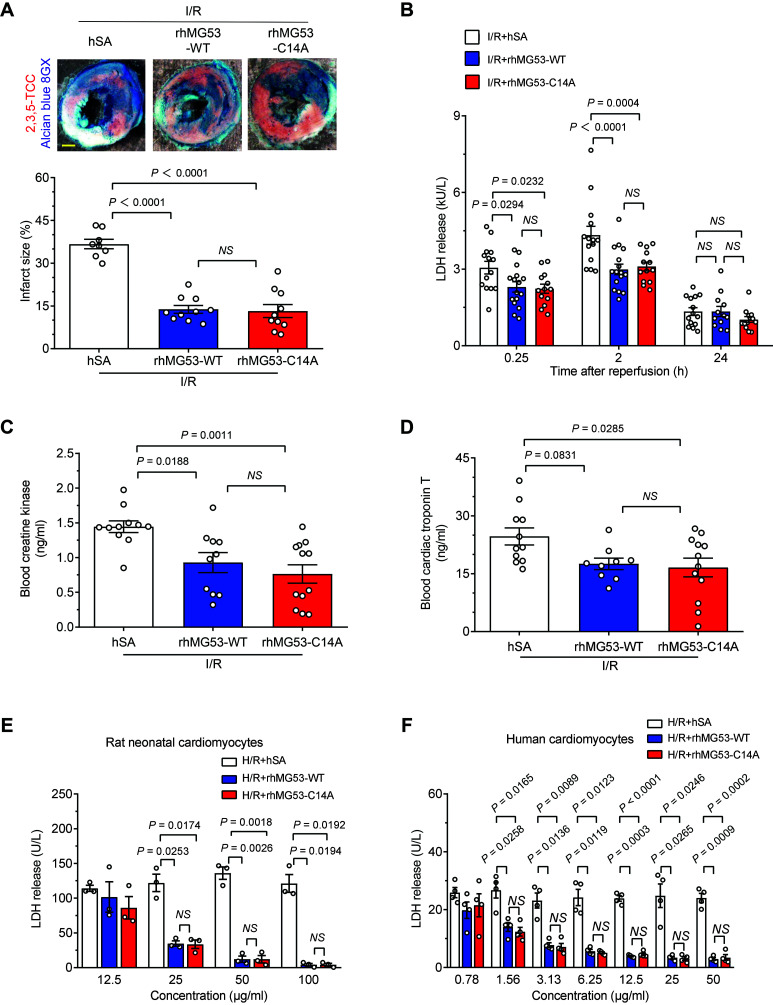
Figure 1.
rhMG53-C14A preserves its protective effect on nondiabetic mouse hearts and cultured cardiomyocytes. A–D: Representative images and statistical data of myocardial infarct size (n = 8, 10, and 10 for I/R + hSA, I/R + rhMG53-WT, and I/R + rhMG53-C14A, respectively, from nondiabetic db/+ mice; the order of the groups is the same in all the panels) (A), serum LDH levels (n = 14, 16, and 13, respectively) (B), blood CK (n = 11, 10, and 12, respectively) (C), and cTnT levels (n = 11, 9, and 12, respectively) (D) induced in vivo by I/R in combination with 1 mg/kg (i.p.) hSA, rhMG53-WT, or rhMG53-C14A treatment. Scale bar is 1 mm. E and F: Levels of LDH release from either cultured rat neonatal cardiomyocytes (data are representative of three independent experiments) (E) or human cardiomyocytes (data are representative of four independent experiments) (F) subjected to H/R with hSA, rhMG53-WT, or rhMG53-C14A treatment at different concentrations. All data are presented as mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was conducted by one-way ANOVA with Tukey multiple comparisons test (A, C, and D) or two-way ANOVA with Tukey multiple comparisons test (B, E, and F). NS, not significant.