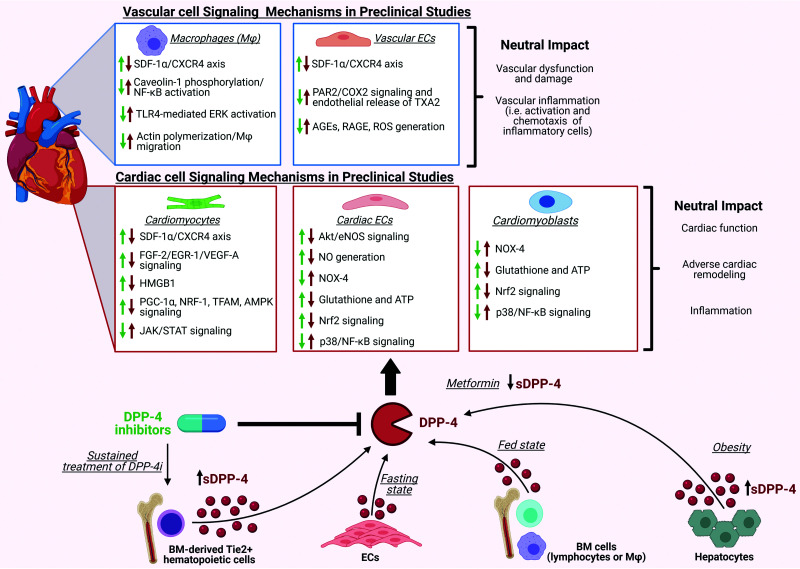
Figure 3.
Potential mechanisms underlying the neutral cardiovascular actions of DPP-4 and DPP-4i. In healthy animals, several pathways within the cardiovascular system have been identified that mediate the effects of DPP-4is; however, the majority have not translated to benefits in subjects with T2DM. Inhibition of DPP-4 in preclinical studies facilitates the homing of CXCR4+ progenitor stem cells at sites of myocardial damage, prevents cardiomyocyte apoptosis, and improves postischemic recovery of cardiac contractility through increasing SDF-1α levels. In addition, DPP-4i can activate Akt/endothelial NO synthase (eNOS) signaling along with NO generation by the endothelium, enhancing FGF-2/EGR-1/VEGF-A signaling, inhibiting HMGB1 inactivation, promoting signaling pathways related to PGC-1α/NRF-1/TFAM/AMPK, downregulating the JAK/STAT signaling pathway, reducing the expression of NOX-4, and restoring intracellular levels of antioxidant glutathione as well as ATP. Furthermore, DPP-4i can reduce p38/NF-κB signaling while inducing Nrf2 signaling. Additionally, DPP-4i can inhibit PAR2/NF-κB signaling cascades, TLR4-mediated extracellular signal–regulated kinase activation, and the expression levels of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) as well as their receptor, RAGE. DPP-4i can also cause macrophage activation and chemotaxis. Despite the identification of many signaling pathways in cell and preclinical models, in MACE trials neutral outcomes are observed. Adding to the complexity of signaling, sDPP-4 may originate from various sources, such as endothelial cells, bone marrow cells, or hepatocytes, depending on the metabolic states, and activate the complementary pathways. Additionally, sustained treatment of DPP-4i also increases sDPP-4 shedding from bone marrow-derived Tie2+ hematopoietic cells; conversely, metformin decreases sDPP-4 levels. The green arrows represent the effects of DPP-4i, whereas the red arrows represent the effects of sDPP-4 on the cardiovascular system. Generated with BioRender (biorender.com; publication license FF233Q5E1I).