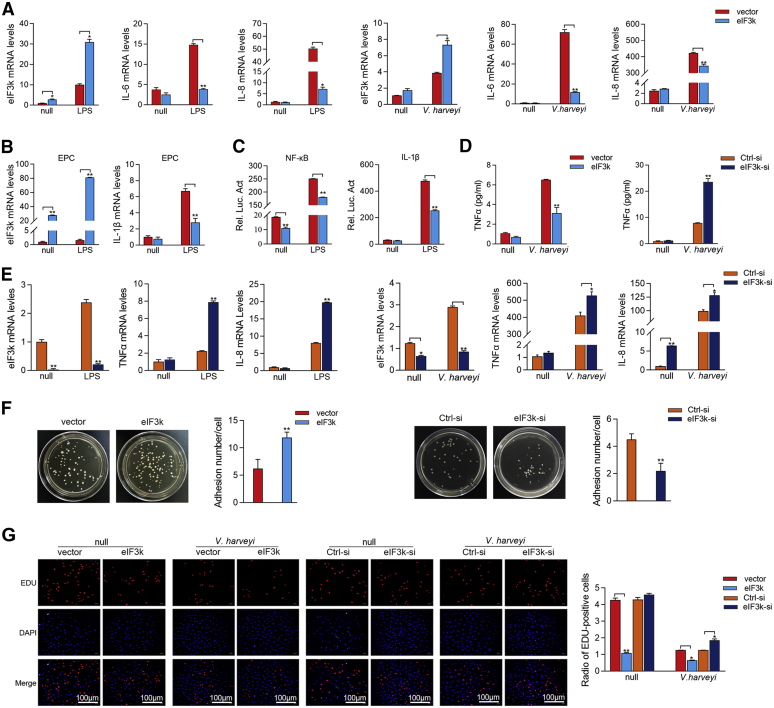
Figure 2.
eIF3k inhibits NF-κB signaling to promote V. haveryi reproduction.A, eIF3k inhibited LPS- and V. harveyi-triggered transcription of pro-inflammatory cytokine in the NF-κB signaling pathway. MIC cells were transfected with eIF3k (500 ng) or control vector pcDNA3.1 (500 ng). Cells were treated with10 μg/ml LPS or V. harveyi for additional 6 h at 36 h post-transfected. eIF3k, IL-6 and IL-8 mRNAs were analyzed by qPCR. B, EPC cells were transfected and stimulate as in (A), eIF3k and IL-1β mRNAs were determined by qPCR. C, eIF3k inhibits LPS-triggered activation of NF-κB and IL-1β reporter gene. EPC cells were transfected with NF-κB, IL-1β reporter gene plasmid, together with pRL-TK Renilla luciferase plasmid. Cells were treated with LPS for an additional 6 h at 24 h post-transfected, followed by detection of luciferase activity. D, TNFα production was detected by ELISA assay in eIF3k overexpression and silenced with V. harveyi infection for 24 h. E, knockdown of eIF3k significantly enhanced LPS- and V. harveyi-triggered transcription of proinflammatory cytokine in MIC cells. Cells were transfected with eIF3k-si, Ctrl-si was used for control. Stimulation with LPS and V. harveyi as before, TNFα and IL-8 mRNAs was determined by qPCR. F, eIF3k increases the adhesion of V. harveyi to MKC cells. Cells were transfected with eIF3k or eIF3k-si, vector and Ctrl-si was used for control. Lysates from V. harveyi infected cells were incubated on LB plates for 12 h, and the colony forming unit (cfu) was counted. G, both bacteria and eIF3k inhibit the proliferation of MKC cells. Cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids for 24 h and infected with V. harveyi for 6 h prior to the cell proliferation assay; Scale bar, 100 μm. The data are shown as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. (∗) p< 0.05, (∗∗) p< 0.01 versus the controls. eIF3k, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3k; EPC, epithelioma papulosum cyprini; MIC, M. miiuy intestine cell; MKC, M. miiuy kidney cell.