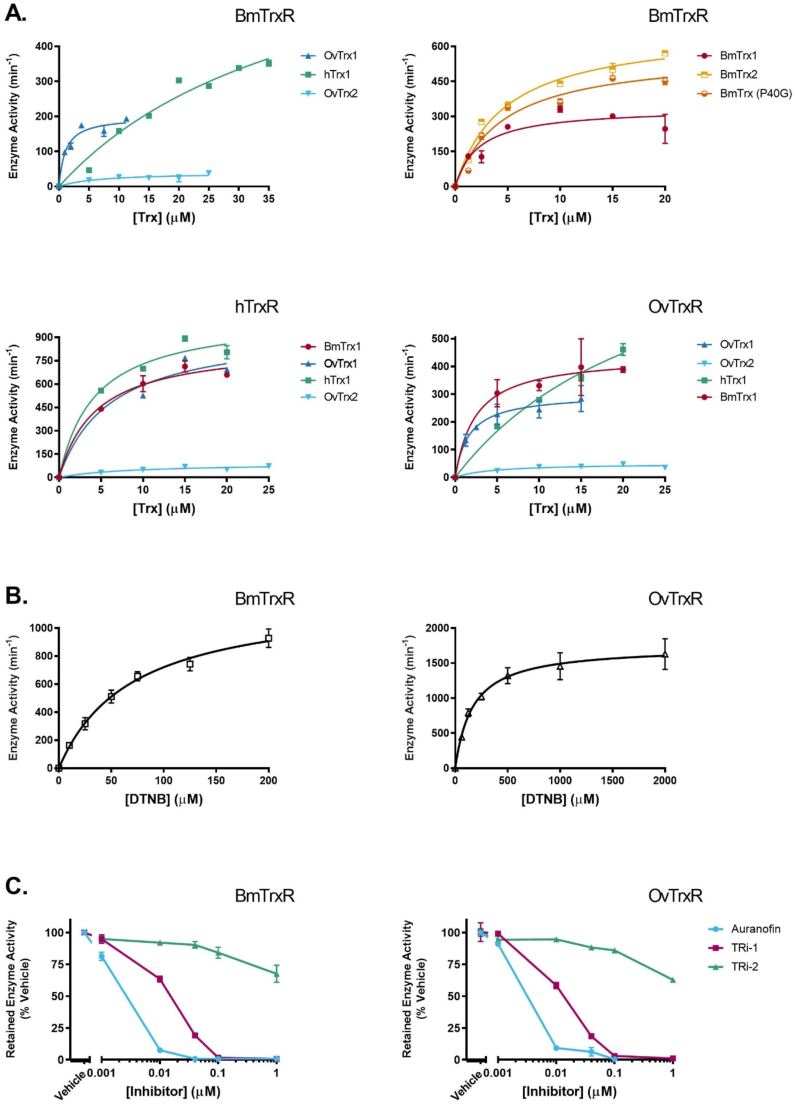
Fig. 3.
Enzyme activity of BmTrxR (isoform D), OvTrxR (isoform D) and hTrxR with substrates (A–B) and inhibitors (C). A: Enzyme activities with BmTrx1, BmTrx2, mutant BmTrx (P40G), OvTrx1 and hTrx1 were measured with 0.25 mM NADPH, 0.16 mM insulin, and 20 nM TrxR (except for 40 nM BmTrxR with OvTrx1), by following A340 and using a NADPH standard curve. Enzyme activities with OvTrx2 were measured with 0.25 mM NADPH, 0.16 mM insulin and 80 nM of TrxR, by following A340 and using a NADPH standard curve. B: Enzyme activities with DTNB were measured with 10 nM OvTrxR or 20 nM BmTrxR and 0.25 mM NADPH, by following A412 for 5 min and using εA412 = 13,600 M−1cm−1. C: Inhibition of 1 mM DTNB reduction by auranofin, TRi-1 or TRi-2, when incubated with 25 nM OvTrxR or BmTrxR for 30 min with 0.25 mM NADPH and 0.1 mg/ml BSA. Relative enzyme activity was assessed by following A412 upon addition of DTNB and normalized to controls incubated with 1% v/v DMSO (vehicle). Error bars represent standard deviation of the mean.