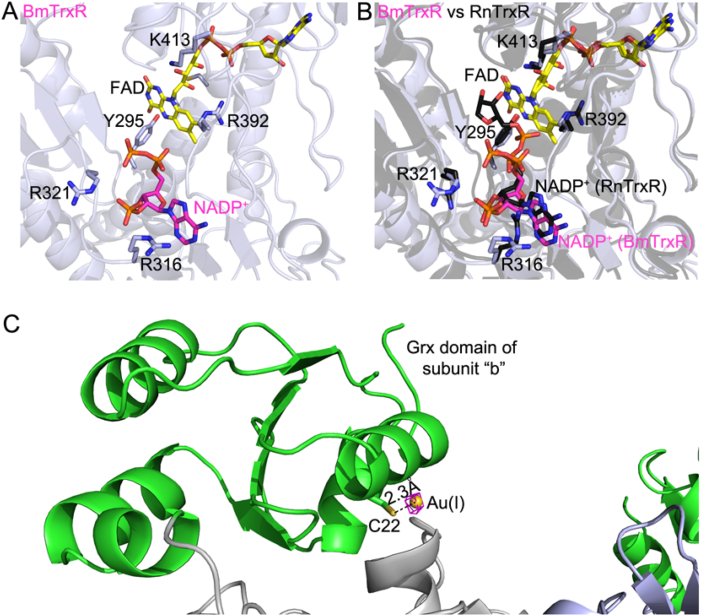
Fig. 7.
BmTrxR in complex with NADP+ and Au(I) from auranofin. In panel A, the NADP(H) binding site of BmTrxR is shown. The BmTrxR structure is colored in light blue, FAD and the bound NADP+ are in yellow and magenta sticks, respectively, while the conserved residues important for binding of the reductant are in light blue sticks (heteroatoms are in CPK colors). In panel B, the superposition of BmTrxR and TrxR from Rattus norvegicus in complex with NADP+ is shown (RnTrxR; PDB ID: 1h6v) [35]. RnTrxR is in black and bound NADP+ is in black sticks, as are the conserved residues interacting with it (numbering is according to the BmTrxR). In this case, the ribose bound to nicotinamide is also visible. In panel C, the BmTrxR-gold complex is shown. The anomalous difference Fourier map contoured at 7σ is shown in magenta meshes. The gold atom, shown as yellow sphere, is at 2.3 Å from the sulfur of C22 and its localization superposes with the anomalous Fourier maps. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)