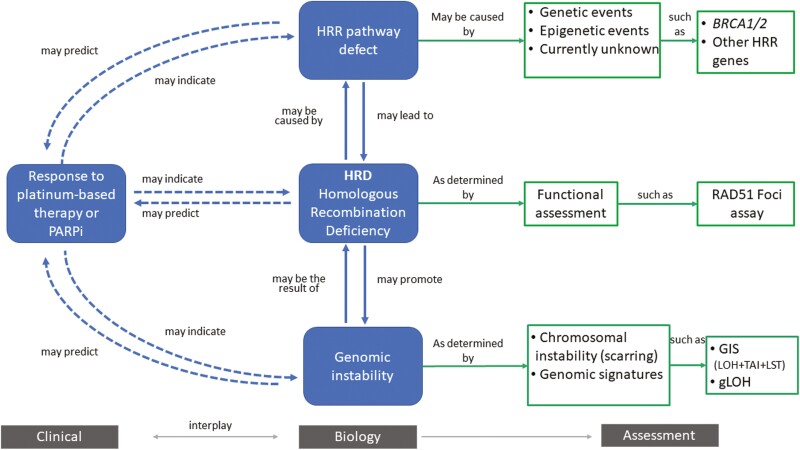
Figure 2.
Overview of homologous recombination deficiency (HRD). Homologous recombination deficiency is a phenotype that is characterized by the inability of a cell to effectively repair double-strand DNA breaks using the homologous recombination repair (HRR) pathway. Alterations in these genes have been deemed “causes” of HRD (eg, genetic events and epigenetic events). This can result in an impaired HRR pathway, which can be deemed “consequences,” and assessed by probing the genome for evidence of genomic instability (eg, chromosomal instability and other genomic signatures).