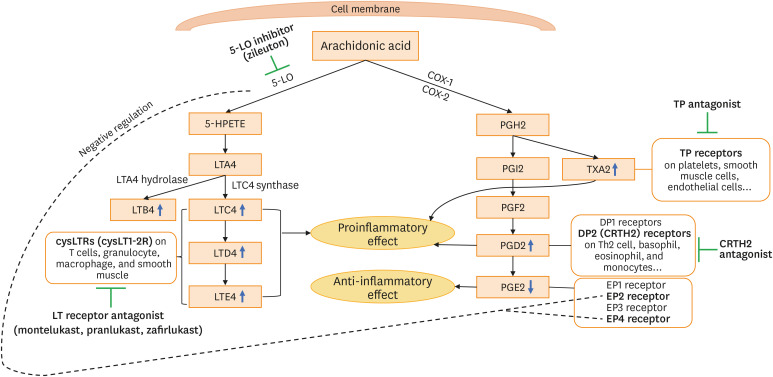
Fig. 1. Arachidonic acid metabolism and therapeutic approach for the management of NERD. Arachidonic acid metabolism is initiated by 2 major enzymes, COX and 5-LO. 5-LO enzyme generates LTA4, which is then converted to LTC4 by LTC4 synthase. LTC4 is metabolized in the order of LTD4 and LTE4. LTC4, LTD4, and LTE4 are designated as cysLT. LTA4 can also be converted to LTB4 by LTA4 hydrolase. COX (COX-1 and COX-2) catalyzes arachidonic acid to PGG2 and subsequently PGH2, which can be further metabolized into PGI2, PGF2, PGD2, PGE2, and TXA2 by corresponding specific synthases. NERD is characterized with systemic elevations in PGD2 along with reduction in PGE2 and overproduction of cysLTs. The inhibition of the COX pathway results in the reduction in PGE2 production and excessive production of cysLTs in NERD.
COX, cyclooxygenase; LO, lipoxygenase; LT, leukotriene; cysLT, cysteinyl leukotriene; PG, prostaglandin; TX, thromboxane; NERD, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-exacerbated respiratory disease; TP, thromboxane prostanoid; DP, D-prostanoid; CRTH2, chemoattractant receptor-homologous molecule expressed on TH2 cells; HPETE, hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acid.