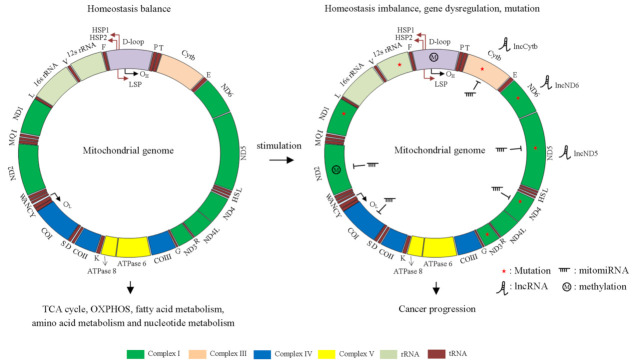
Figure 1.
Overview of the human mitochondrial genome, including protein-coding genes, noncoding RNAs and control regions. The mtDNA is double-stranded and circular, with approximately 16,569 base pairs, which encode 2 rRNAs, 22 tRNAs and 13 mitochondrial protein subunits. The rRNA genes are in teal. Complex I genes are in green. Complex III genes are in peach buff. Complex IV genes are in blue. Complex V genes are in yellow. The regulatory region, D-loop, is shown in amethyst. Two promoters in mtDNA, heavy strand promoters (HSP) and light strand promoters (LSP), are shown. Left panel: Normal mitochondria functions as regulators for maintaining cellular homeostasis, such as the TCA cycle, OXPHOS and fatty acid metabolism. Right panel: Mitochondrial DNA mutations (red star), mitochondrial genes dysfunction and methylation lead to homeostasis imbalance and cancer progression. F: tRNA Phe, V: tRNA Val, L: tRNA Leu, I: tRNA Ile, Q: tRNA Gln, M: tRNA Met, W: tRNA Trp, A: tRNA Ala, N: tRNA Asn, C: tRNA Cys, Y: tRNA Tyr, S: tRNA Ser, D: tRNA Asp, K: tRNA Lys, G: tRNA Gly, R: tRNA Arg, H: tRNA His, S: tRNA Ser, L: tRNA Leu, E: tRNA Glu, T: tRNA Thr and P: tRNA Pro.