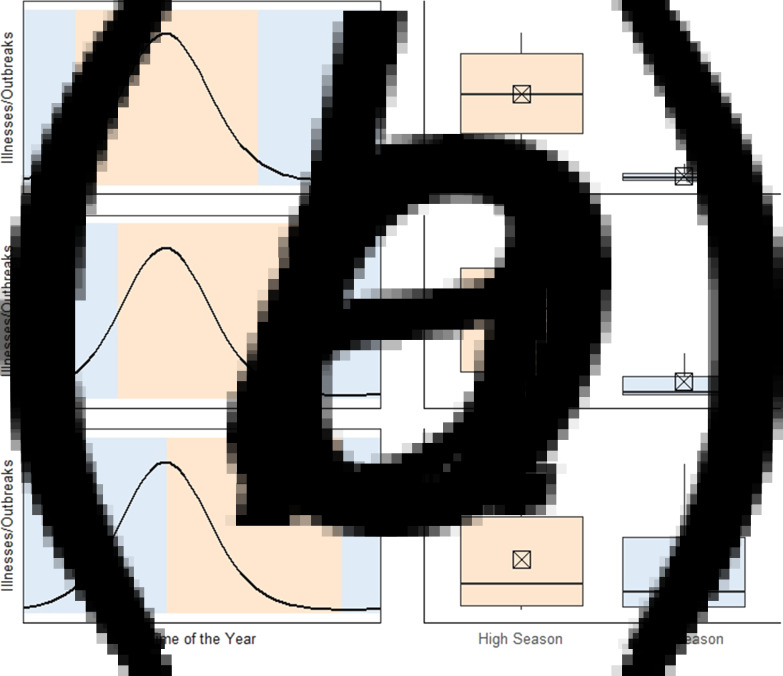
Fig. 2.
An illustration of detecting seasonality and estimating seasonal peak timing using two discrete seasons. Scenarios include (a) when peak and nadir timing align with the centre of each season, as expected for incidence-based definitions of seasons; (b) when peak and nadir timing is shifted from the centre of each season; and (c) when peak timing aligns with the boundary between seasons and results in substantial misclassification bias.