Figure 2.
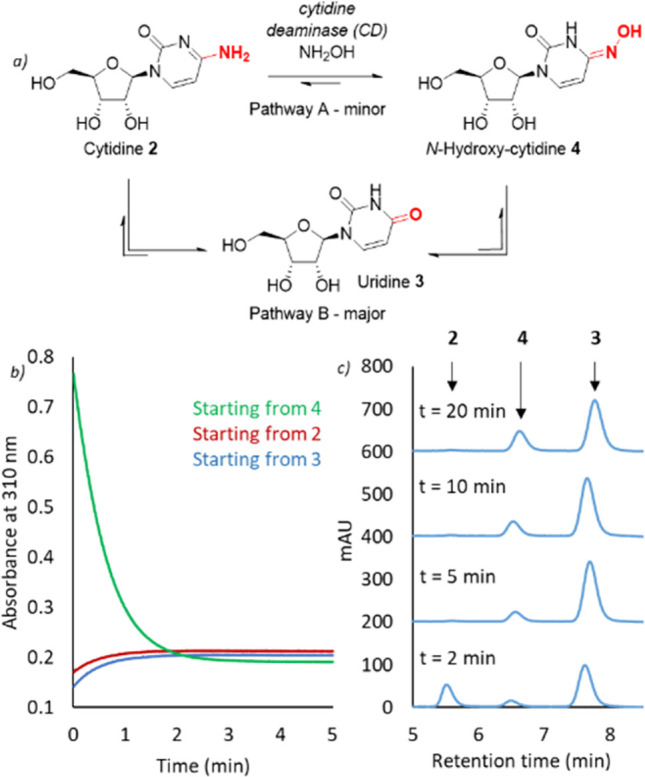
Characterization of wild-type cytidine deaminase (CD). (a) Pathways for conversion of 2 to 4 catalyzed by CD. Pathway A involves direct conversion of 2 to 4 using NH2OH as a nucleophile. Pathway B involves initial hydrolysis of 2 to uridine 3, which is then transformed to 4 through condensation with NH2OH. Pathway B is the dominant pathway when using the wild-type enzyme, leading to an equilibrium distribution of 3 and 4. (b) The conversion of 2 (1 mM) and 3 (1 mM) to 4 by CD (5 μM) in the presence of 1% NH2OH (∼300 mM, pH 7) is monitored by increasing absorbance at 310 nm. Similar final concentrations of 4 are formed using either 2 (red) or 3 (blue) as a starting material, or in reactions starting from 4 (green). (c) The conversion of 2 (750 mM) by CD (25 μM) to 3 and 4 is monitored by HPLC analysis in the presence of 10% NH2OH (∼3 M, pH 7). The time course of the reaction indicates CD operates via pathway B.
