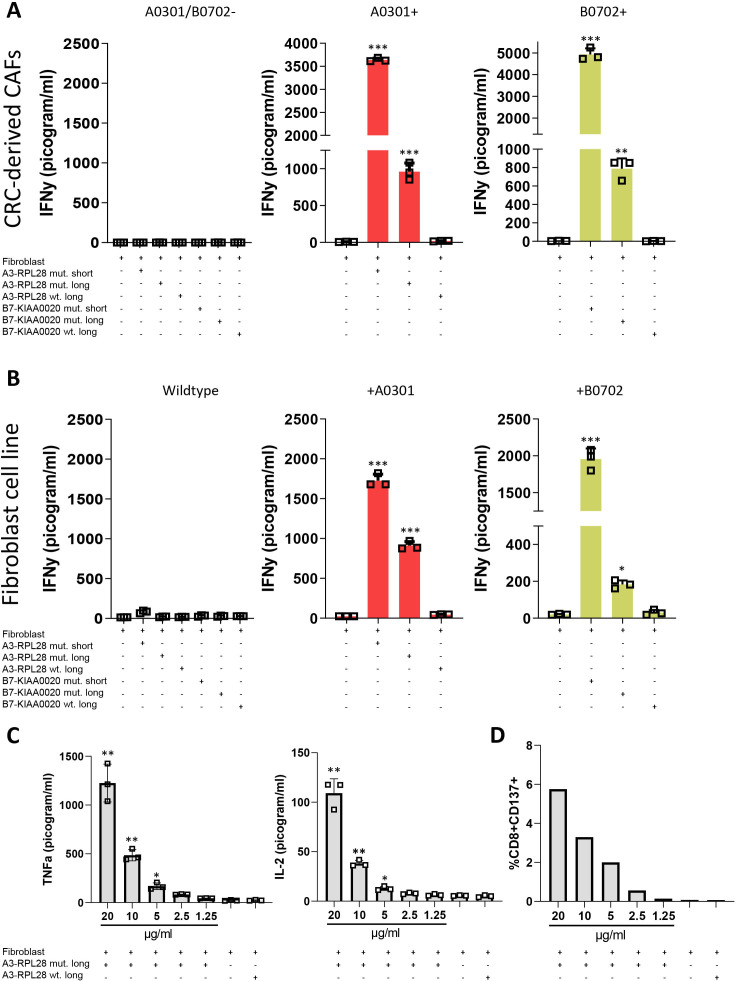
Figure 1.
Human CRC-derived CAFs induce neoantigen-specific T cell activation. (A) IFNγ production by neoantigen-specific T cells (T-cell bulk reactive to both the A3 and B7-epitopes) after 24 hours coincubation with antigen presenting human CRC-derived CAFs (20 µg/mL SLP, 2 µg/mL SSP). The different panels show different primary CRC-derived CAFs with differential HLA-haplotypes. Experimental conditions are compared with the T cell—fibroblast only condition with 1-way ANOVA *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. (B) IFNγ production of neoantigen-specific T cells (T-cell bulk reactive to both the A3 and B7-epitopes) after 24 hours coincubation with the antigen presenting NBS fibroblast line (20 µg/mL SLP, 2 µg/mL SSP). The different panels show wildtype, HLA-mismatched fibroblasts and fibroblasts that have been transduced to express the correct HLA-molecule needed for presentation. Experimental conditions are compared with the T cell—fibroblast only condition with one-way ANOVA *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. (C) TNFα and IL-2 production by neoantigen-specific T cells after 24 hours coincubation with the antigen presenting HLA-A3+ NBS fibroblast line. Concentration of peptide used for the mutant SLP is depicted. Concentration for wildtype SLP is 20 µg/mL. Experimental conditions are compared with the T cell—fibroblast only condition with Student’s t-test **=p≤0.001, *=p≤0.05. (D) Surface CD137-expression on neoantigen-specific T cells after coincubation with antigen presenting NBS fibroblasts determined by FACS. Concentration of peptide used for the mutant SLP is depicted. Concentration for wildtype SLP is 20 µg/mL. Data are plotted from representative experiments performed with one replicate per condition (n=3). ANOVA, analysis of variance; CAFs, cancer-associated fibroblasts; CRC, colorectal cancer; NBS, Nijmegen Breakage Syndrome; SLP, synthetic long peptides.