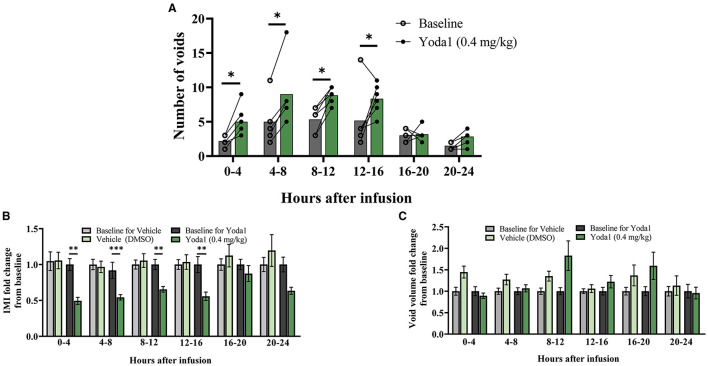
Figure 1.
Intravesical infusion of Yoda1 alters voiding function. The voiding function of conscious, freely moving, rats was studied for 24 h post saline infusion (baseline) and compared to voiding function following Yoda1 (0.4 mg/kg) or vehicle (5% DMSO in saline) infusion. (A) In naïve (no CYP) female rats (n = 6), activation of PIEZO1 with the agonist Yoda1 significantly increases number of voids at every timepoint studied until 16 h after infusion (P ≤ 0.05). (B) This increase in number of voids is matched by a significant decrease in the IMI at the same timepoints (P ≤ 0.01, 0–4, 8–12, and 12–16 h, and P ≤ 0.001 4–8 h post infusion) compared to vehicle infusion (n = 7). (C) These changes in voiding frequency after Yoda1 infusion do not result in any changes in void mass at any timepoint studied compared to vehicle infusion. Values are means ± SEM. Statistical analyses were performed using mixed model repeated measures ANOVA on square root (A) or natural log (B,C) transformed data. Fold-change transformation in (B,C) was done post-statistical analysis. *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001.