Figure 2.
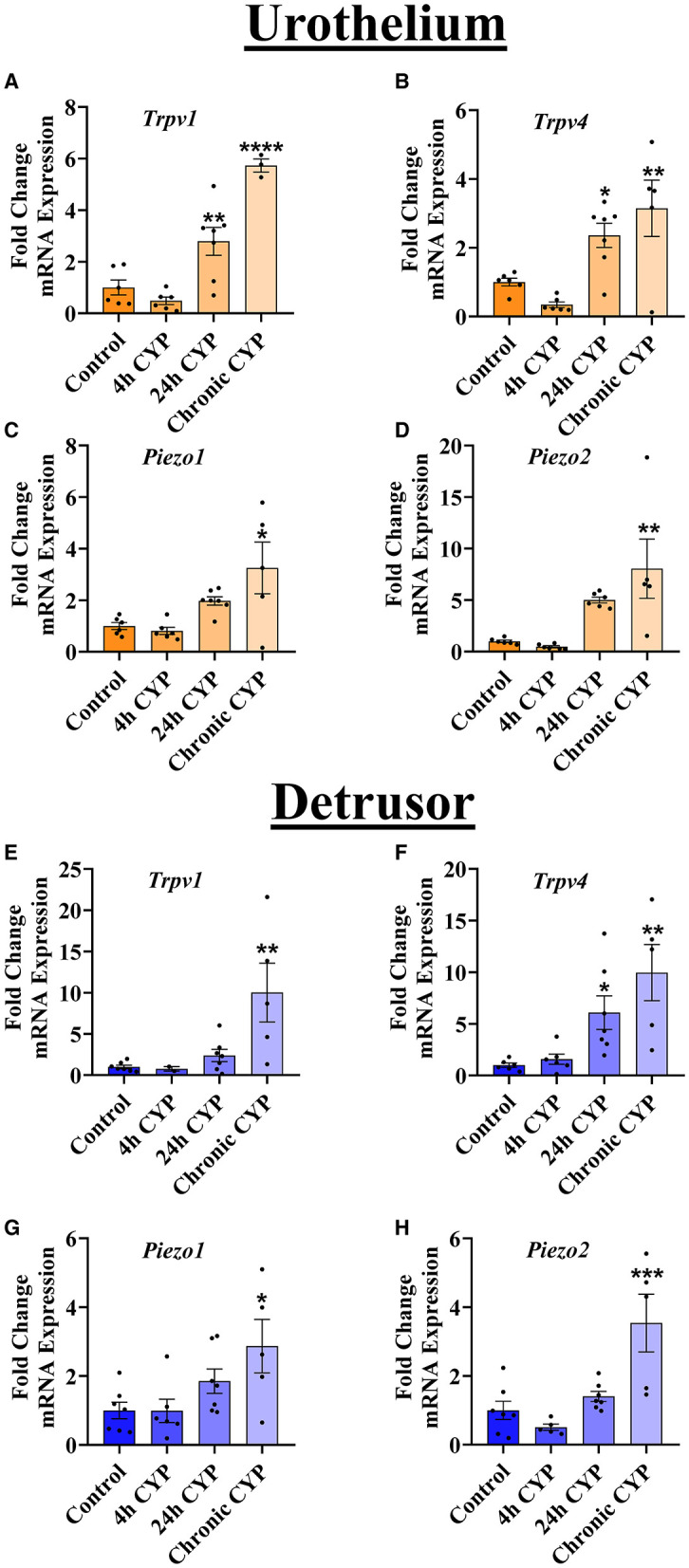
Chronic, but not acute, CYP-induced cystitis leads to increases in MSC gene expression. RT-qPCR was used to detect MSC mRNA separately in the urothelium and the detrusor layers of the urinary bladder at several timepoints of CYP treatment. (A–D) In the urothelium, Trpv1 (n = 3–7) and Trpv4 (n = 5–7) mRNA were significantly upregulated after 24 h CYP-treatment (P ≤ 0.01 and P ≤ 0.05, respectively) and after chronic CYP-induced cystitis (P ≤ 0.0001 and P ≤ 0.01, respectively). Piezo1 (n = 5–7) and Piezo2 (n = 5–6) were both significantly increased in the urothelium only after chronic CYP-treatment (P ≤ 0.05 and P ≤ 0.01, respectively). (E–H) In the detrusor, Trpv1 (n = 2–7) was increased after chronic CYP-treatment (P ≤ 0.01), whereas Trpv4 (n = 5–7) was increased following both 24 h CYP-treatment (P ≤ 0.05) and chronic CYP-induced cystitis (P ≤ 0.01). Piezo1 (n = 5–7) and Piezo2 (n = 5–7) mRNA were also both significantly upregulated in the detrusor following chronic CYP-induced cystitis (P ≤ 0.05, and P ≤ 0.001, respectively). Values are means ± SEM. Data were normalized to a housekeeping gene (L32) and statistical analyses were performed on raw data using a One-Way ANOVA before fold-change transformation. *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001; ****P ≤ 0.0001.
