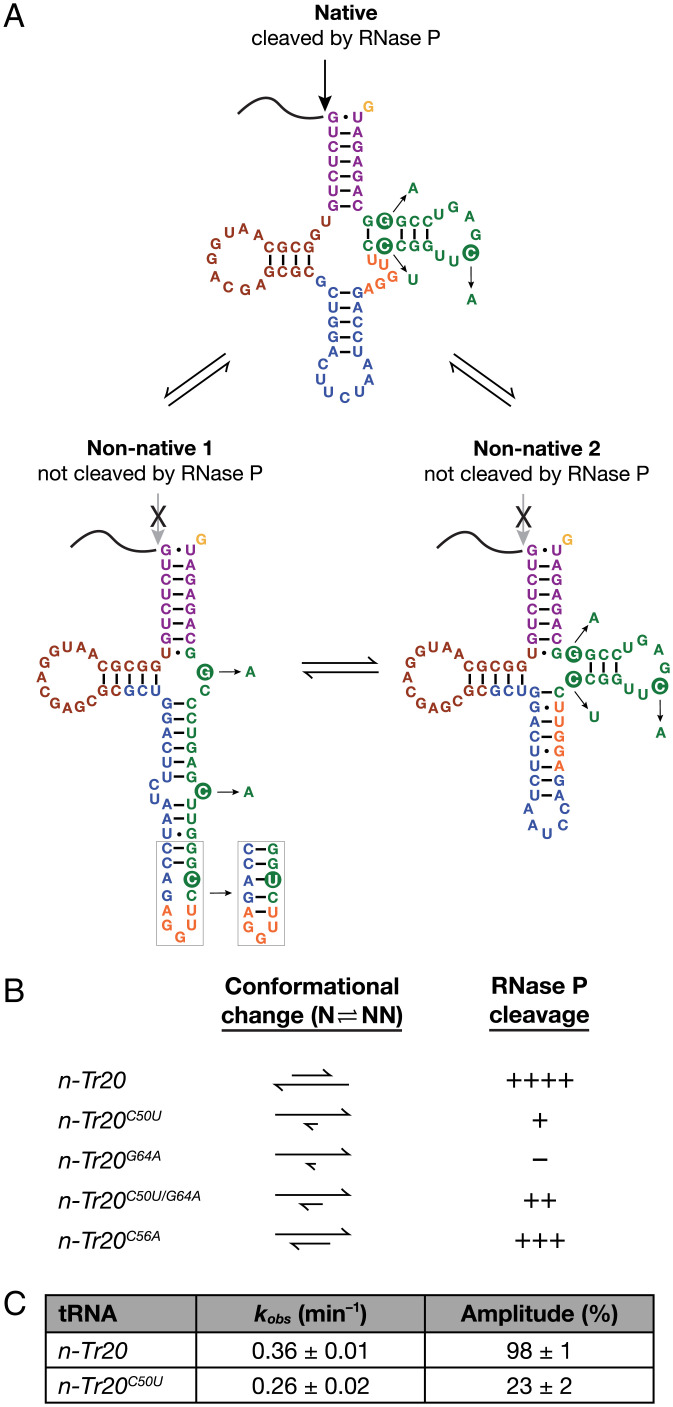
Fig. 4.
Postulated nonnative conformers of n-Tr20 and its mutant derivatives. (A) n-Tr20 may toggle between the native (favored in the presence of Mg2+) and several nonnative conformations, including the two shown here. Both nonnative configurations likely lack the native tRNA elbow, a key recognition determinant necessary for RNase P cleavage (22–24). (B) The propensity of mouse RNase P to cleave each n-Tr20 variant (data are from Fig. 2B) likely reflects the proportion of tRNA that adopts the native conformation. Cleavage efficiency: ++++, fully competent; +/++/+++, partially competent to varying extents; –, defective. N, native structure; NN, nonnative structure. (C) Summary of data from single-turnover kinetic studies conducted with in vitro–reconstituted E. coli RNase P in 5 mM Mg2+ and at pH 5.5. Mean and standard deviation values were determined from three independent measurements.