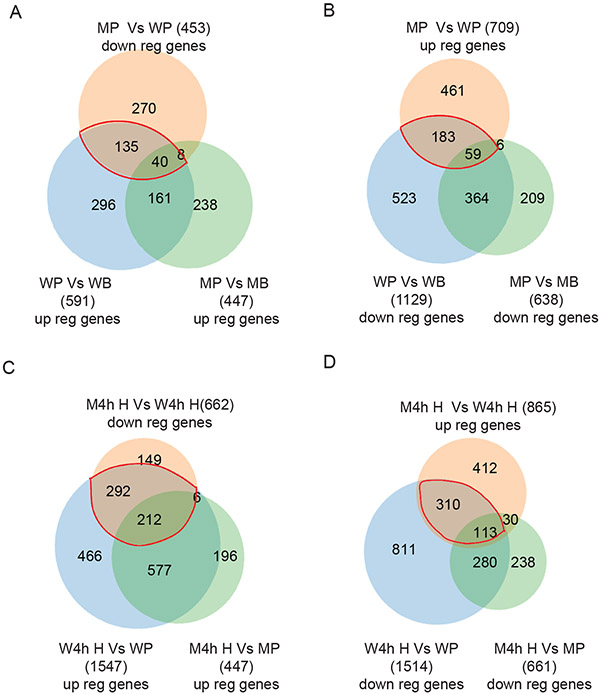
Figure 3. Identification of PMSG- and hCG-regulated genes that are dependent on ERβ signaling.
Upregulated (up reg) genes from the Basal to PMSG treated group in wildtype (WP vs WB) granulosa cells (GCs) were compared with that of Erβnull GCs (MP vs MB). These two sets of DEGs were then compared with the genes that were differentially downregulated (down reg) in PMSG-treated Erβnull GCs compared to that of wildtype GCs (MP vs WP) to identify the potential PMSG-induced genes that are dependent on ERβ signaling (A). Downregulated genes from the Basal to PMSG group in wildtype GCs (WP vs WB) were compared with that of Erβnull GCs (MP vs MB). These two sets of DEGs were then compared with the genes that were upregulated in PMSG-treated Erβnull GCs (MP vs WP) to identify the PMSG-inhibited genes that are dependent on ERβ (B). Similarly, upregulated genes in PMSG to hCG 4h wildtype GCs (W4h H vs WP) were compared to that of Erβnull GCs (M4h H vs MP), and subsequently compared with the genes downregulated in Erβnull GCs 4h after hCG treatment (M4hH vs W4h H), to identify the hCG-induced genes that are dependent on ERβ (C). Finally, downregulated genes from PMSG to hCG 4h wildtype GCs (W4h H vs WP) were compared to that of Erβnull GCs (M4h H vs MP), and then with the differentially upregulated genes in Erβnull hCG 4h GCs (M4h H vs W4h H), to detect the hCG inhibited genes that are dependent on ERβ (D). WB, Wildtype Basal; WP, Wildtype PMSG; W4h H, Wildtype 4h post-hCG; MB, Erβnull Basal; MP, Erβnull PMSG; M4h H, Erβnull 4h post-hCG.