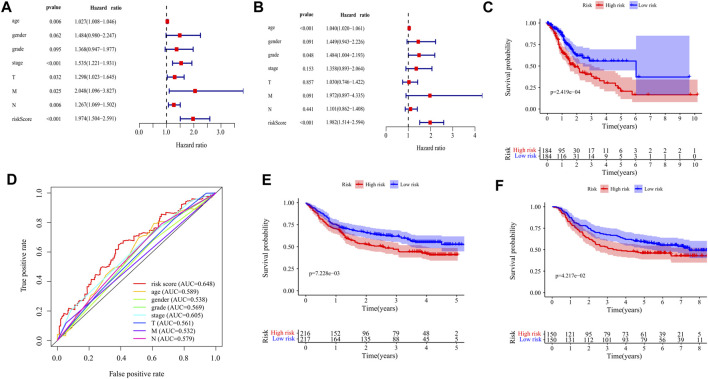
FIGURE 6.
Validation of the prognostic signature of ten DEGs. (A) The Forest plot reflects the univariate Cox analysis of the relationship between the clinical features, risk score, and OS of GC patients. Both stage and risk score significantly affect the prognosis of GC patients (p < 0.001). (B) The Forest plot reflects the multivariate Cox analysis of the relationship between the clinical features, risk score, and OS of GC patients. Age and risk score are independent prognostic risk factors for GC (p < 0.001). (C) The Kaplan-Meier Survival curve shows that the OS of high-risk GC patients is significantly lower than that of low-risk patients. The abscissa represents time (years), the ordinate represents survival probability. (D) The 1-year time-dependent ROC curve shows that the prediction accuracy of the risk score is higher than other clinical features (AUC = 0.648). The abscissa represents false positive rate, the ordinate represents true positive rate. (E) Kaplan-Meier Survival Curve of patients with GC in high-risk and low-risk groups in GSE84437 (p = 7.228e−03). The abscissa represents time (years), the ordinate represents survival probability. (F) Kaplan-Meier Survival Curve of patients with GC in high-risk and low-risk groups in GSE66229 (p = 4.217e−02). The abscissa represents time (years), the ordinate represents survival probability.