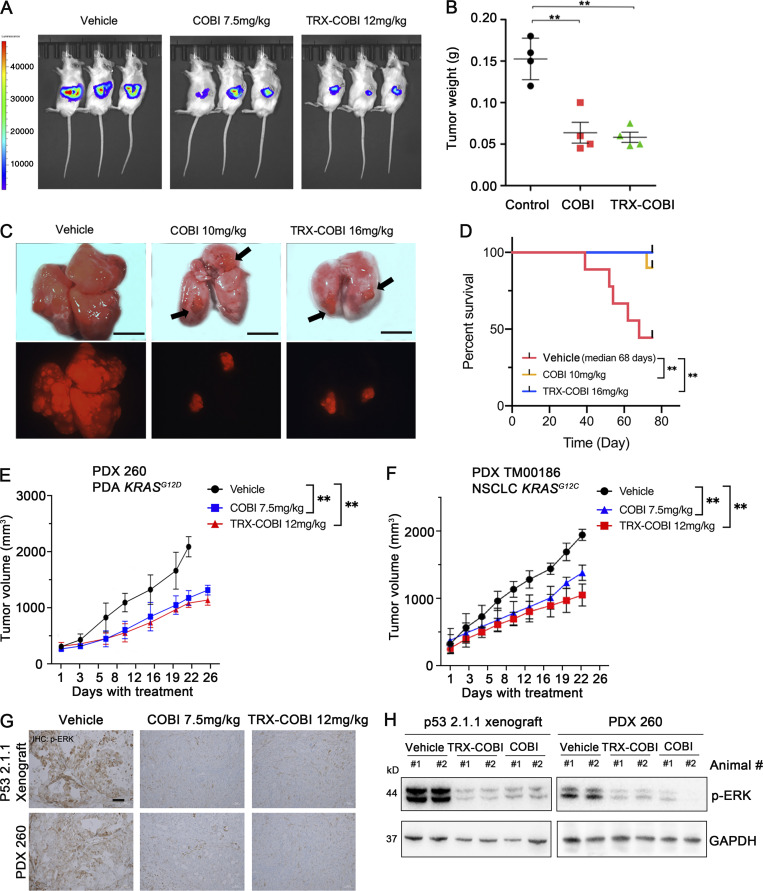
Figure 4.
An FeADC of COBI exhibits potent antitumor activity in vivo. (A) Representative bioluminescence images of p53 2.1.1-fLuc orthotopic pancreas tumor xenografts treated with vehicle or the indicated, equimolar doses of COBI or TRX-COBI. (B) Tumor weights at the end point from A. Error bars represent mean ± SEM, n = 4–5 mice/group and analyzed by a two-sample t-test. **, P < 0.01. (C) Representative gross lung images in KP mouse model. Vehicle, equimolar doses of COBI, and TRX-COBI treatment started 8 wk after the adenoviral induction and continued for 60 d. Scale bar: 0.5 cm. (D) Overall survival of (C) analyzed by a log-rank test, n = 8–10 mice/group; **, P < 0.01. (E and F) Tumor volume changes (mean ± SEM; error bars) of mutant KRAS PDA and NSCLC PDX model, n = 8–10 mice/group. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA; **, P < 0.01. (G) IHC of xenografts from A and E (10×) stained with phosphorylated ERK. Scale bar: 50 µm. (H) Western blot for phosphorylated ERK of tumors resected at the end of treatment in A and E.