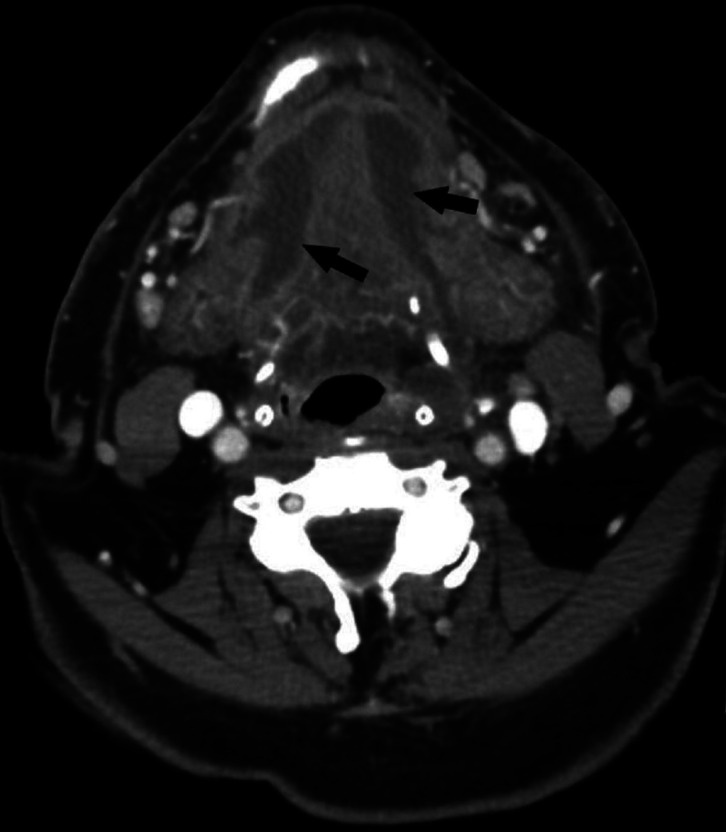
Figure 2.
Two days later the patient reappeared to the dentist due to difficulties in swallowing and mouth opening. Typical findings of Ludwig’s angina were observed: mouth floor swelling, difficulties in speaking and swallowing and limited mouth opening. The dentist referred the patient to hospital. Features of severe infection were detected also in infection parameters: Body temperature was 38.5, C-reactive protein level (CRP) was 342 mg/l and white blood cell count was 19.2 E9/l. Computer tomography images (see also Fig 3.) confirmed the clinical diagnose of bilateral abscess which had spread from the mandibular third molar area (arrows). The airway was also restricted.