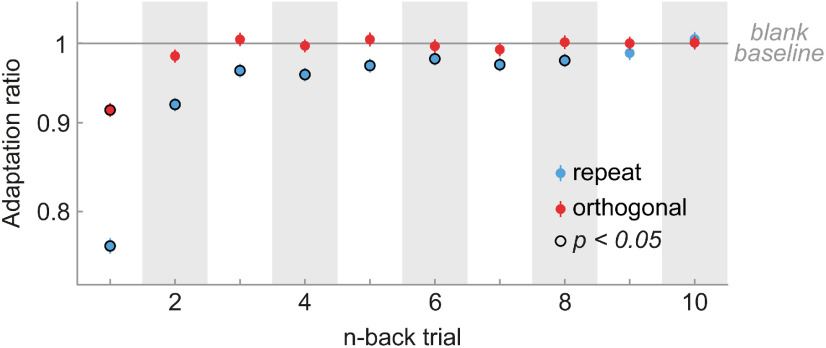
Figure 5.
Cortical long-term adaptation is driven by repeated stimulus orientations. We expressed the response modulation of neurons across all cortical areas by n-back repeated and orthogonal trials relative to a neutral baseline in which no stimulus was presented on the n-back trial. To this end, we computed adaptation ratios by dividing the firing rate of each neuron for repeat stimulus presentations by that of blank stimulus presentations (blue data points) or orthogonal divided by blank stimulus presentations (red data points). Although the suppressive effects of orthogonal stimuli decay quickly, repeated stimuli exert long-term suppression for up to eight trials. Error bars indicate bootstrapped 95% confidence intervals.