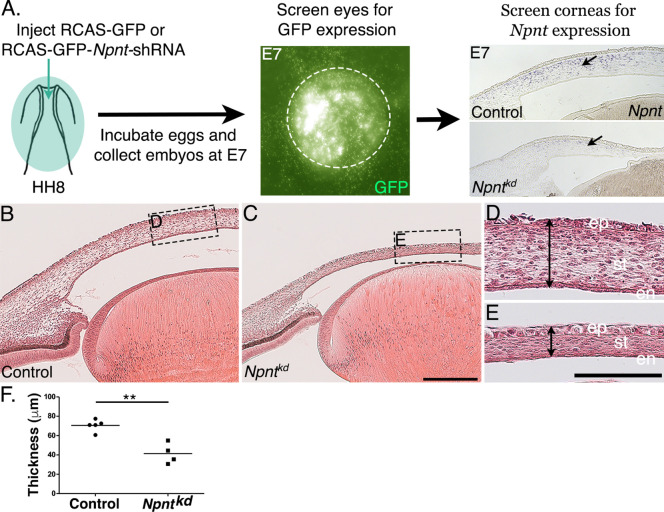
Figure 2. Corneal thickness is reduced in Npntkd corneas.
(A) Schematic of in ovo injection of viral constructs (green) to cover the anterior region of stage 8 chick embryo. Following 7 days of incubation, embryos were screened for GFP expression in the anterior eye region. Knockdown was verified by section in situ hybridization, which revealed reduced expression of Npnt in Npntkd cornea compared with control. (B–E) Hematoxylin and eosin staining showing control (B, D) and thinner Npntkd corneas (C, E). Statistical analysis on measurements taken from (N = 5 control and N = 4 Npntkd corneas) revealed (F) significant reduction in thickness of Npntkd corneas. **p<0.01. ep, corneal epithelium; st, stroma; en, corneal endothelium;. Scale bars: 100 μm (B, C), 100 μm (D, E).