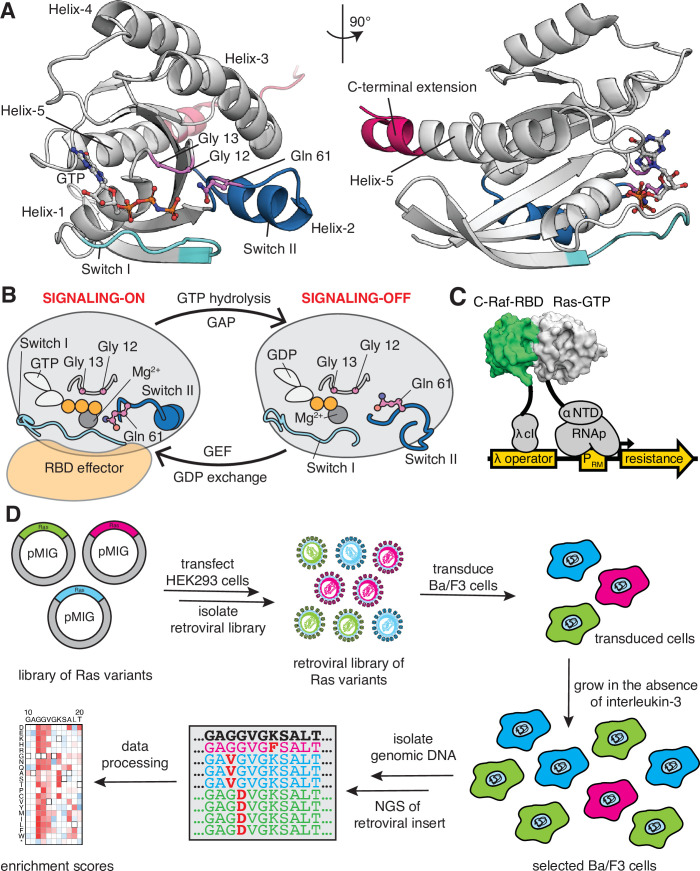
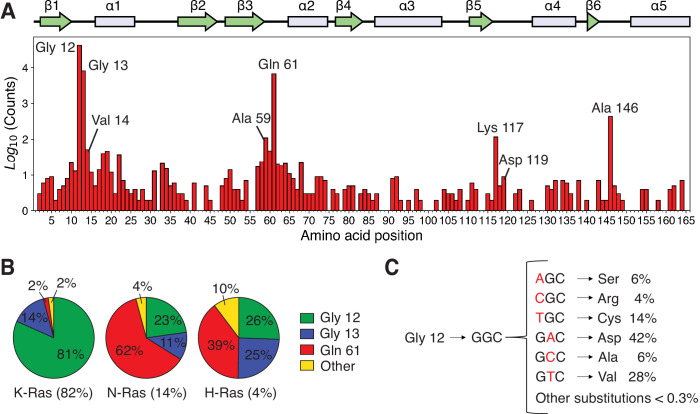
Figure 1. Ras G-domain, the switching cycle, and schematics of the two selection assays.
(A) The three principal sites of cancer mutations in Ras, referred to as the three cancer hotspots – Gly 12, Gly 13, and Gln 61 – are shown in the K-Ras structure. The C-terminal helix extension is indicated. PDB ID: 2MSD (Mazhab-Jafari et al., 2015). (B) Ras cycles between signaling-active GTP-bound and signaling-inactive GDP-bound states. (C) The bacterial-two-hybrid system couples the C-Raf-RBD•Ras-GTP interaction to the transcription of an antibiotic resistance gene (Bandaru et al., 2017). Ras is fused to the N-terminal domain of the α-subunit of the E. coli RNA polymerase. C-Raf-RBD is fused to the λ-cI protein. The GAP and the GEF can be co-expressed in the system. E. coli cells are transformed with a DNA library of ‘unselected’ variants. The bacteria are grown in the presence of an antibiotic for 9 hr, then the DNA library of ‘selected’ variants is isolated. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) is used to count the frequency of each variant in the unselected and selected samples. (D) Ba/F3 assay for Ras activity. Mutant H-Ras libraries are transfected into HEK 293T cells to generate a retroviral library of mutants. Ba/F3 cells are transduced with the retroviral library. After 24 hours, a fraction of the cells are used as the unselected population, and the remainder of the cells – the selected population – are cultured for 7 days in the absence of IL-3 before harvesting them by centrifugation. The genomic DNA of the selected and unselected populations is isolated and sequenced using NGS. The relative enrichment scores are calculated using the selected and unselected counts (see Equation 1).