Figure 1.
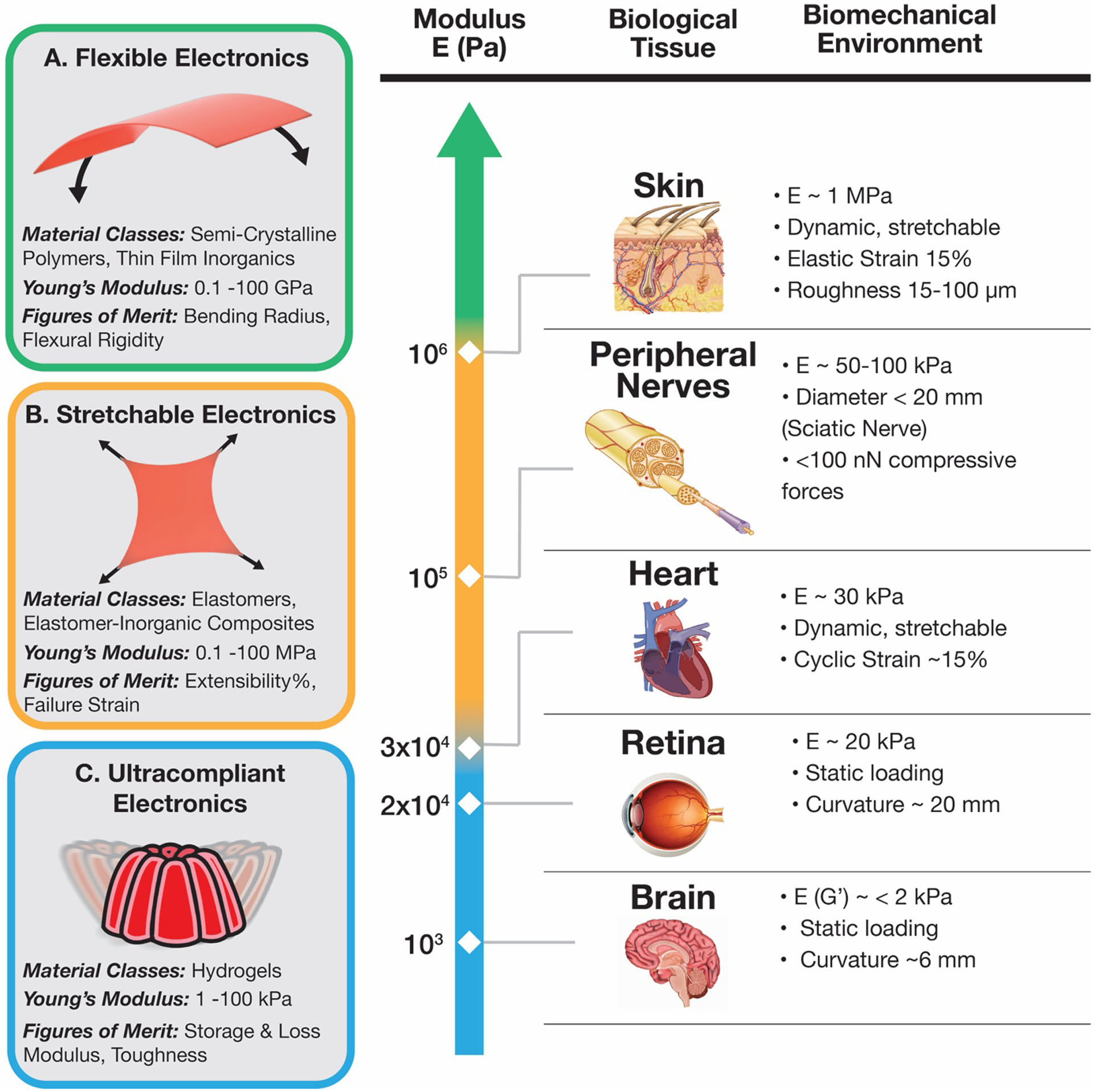
(Left) The mechanical description and figures of merit of three regimes of bioelectronics devices: A. flexible electronics (0.1–100 GPa),[41] B. stretchable electronics (0.1–100 MPa),[39] and C. ultracompliant electronics (1–100 kPa).[59] (Right) A biomechanical description of target organs and loading conditions for mechanically compliant bioelectronics deployment: skin,[60] peripheral nerves,[61–64] heart,[65–67] retina,[68,69] and brain.[70–72] Reproduced with permission.[73] Copyright 2017, Elsevier.
