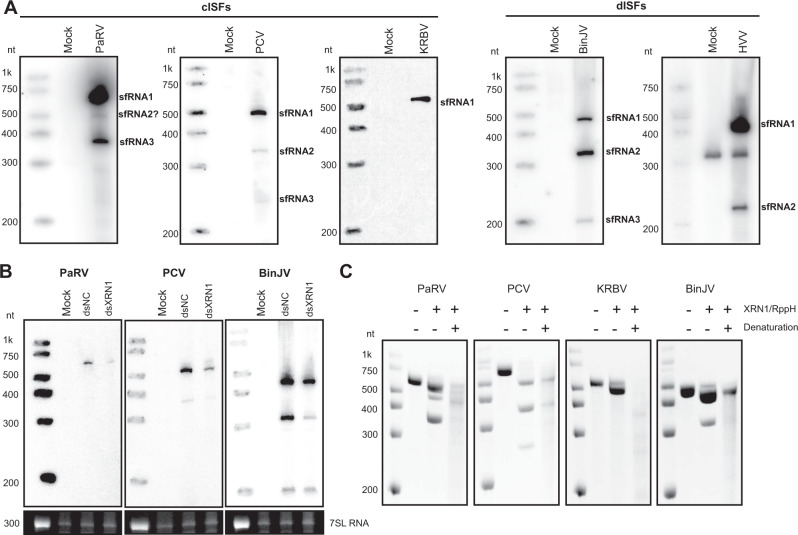
Fig. 1. Classical and dual host-associated ISFs produce sfRNAs by employing XRN1-resistance mechanism.
A Northern blot detection of sfRNAs produced by ISFs. For PaRV, PCV, BinJV and HVV C6/36 cells were infected at MOI = 1. Total RNA was isolated at 5 dpi. For KRBV, total RNA was isolated from virus-positive and virus-negative (Mock) Anopheles mosquitoes. RNA was then used for Northern blotting with the probe complementary to the last 25nt of viral 3’UTRs. B The effect of XRN1 knock-down on the production of sfRNAs by ISFs. Aag2 cells were transfected with dsRNA against Aedes aegypti XRN1 (dsXRN1) or GFP (dsNC) and infected with respective viruses at MOI = 1 at 24hpt. At 48hpi, total RNA was isolated from the cells and used for Northern blotting as in (A). Bottom panels represent the Et-Br staining of the gels used for Northern transfer with 7SL cellular RNA visualised as a loading control. C In vitro XRN1 resistance assay with ISF 3’UTRs. RNA corresponding to 3’UTRs of ISFs was transcribed in vitro, briefly heated and then refolded by gradual cooling to 28 °C or placed on ice to preserve the denatured state. Samples were then treated with purified XRN1 and RppH (to convert 5’PPP into 5’P) and analysed by electrophoresis in denaturing PAAG. Gels were stained with ethidium bromide (Et-Br). All images are representative of at least two independent experiments that produced similar results.