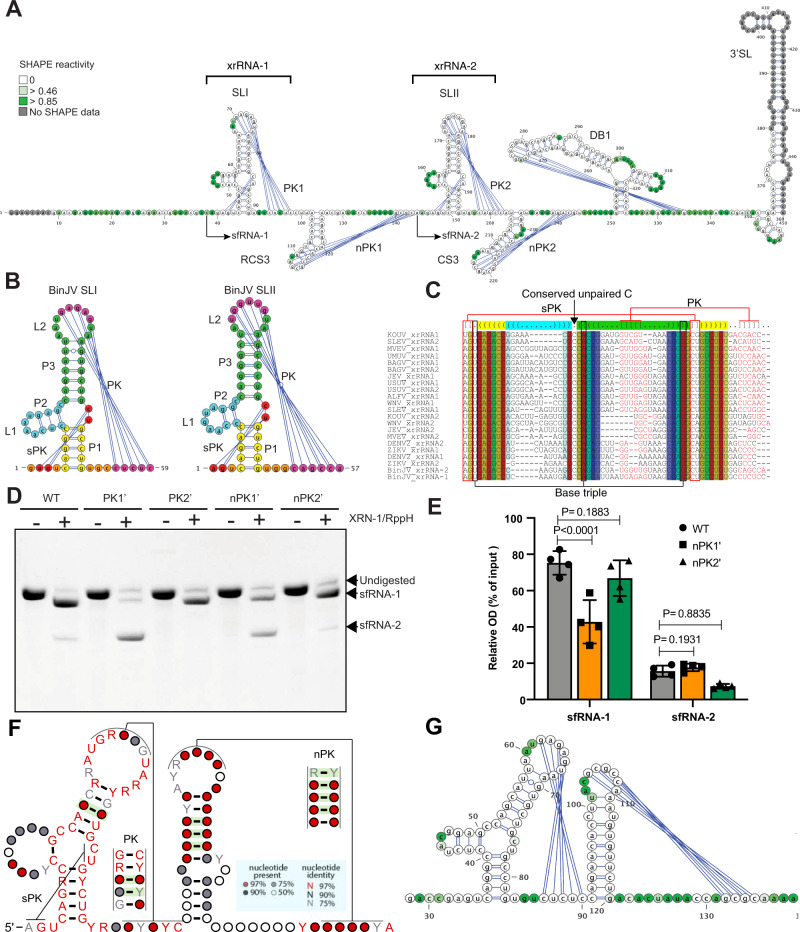
Fig. 2. dISFs contain novel SL-PK elements in addition to canonical class 1a xrRNAs.
A Secondary structure of BinJV 3’UTR generated by SHAPE. SL – stem-loop, DB – dumbbell, RCS3 – reverse conserved sequence 3, CS3 – conserved sequence 3, PK – pseudoknot. B Secondary structures of BinJV stem-loops. C Structure-based sequence alignment between BinJV and MBF xrRNAs. D XRN1 resistance assay with WT and mutated BinJV 3’UTRs. Mutations PK1’ (GAGAG- > CUCUC), PK2’ (UGGUUG- > ACCAAC), nPK1’ (UAGCG- > AUCGC) and nPK2’ (GCGUC- > CGCAG) were introduced into the terminal loop regions of the corresponding stem-loops. The image is representative of four independent experiments that produced similar results. E Densitometry analysis of (D). The values are the means of four independent experiments ± SD. Statistical analysis is two-sided one-way ANOVA. F Consensus structure of dISF xrRNAs built based on the covariance model. Covarying base pairs are highlighted in green (G) Secondary structure of HVV xrRNA generated by SHAPE.