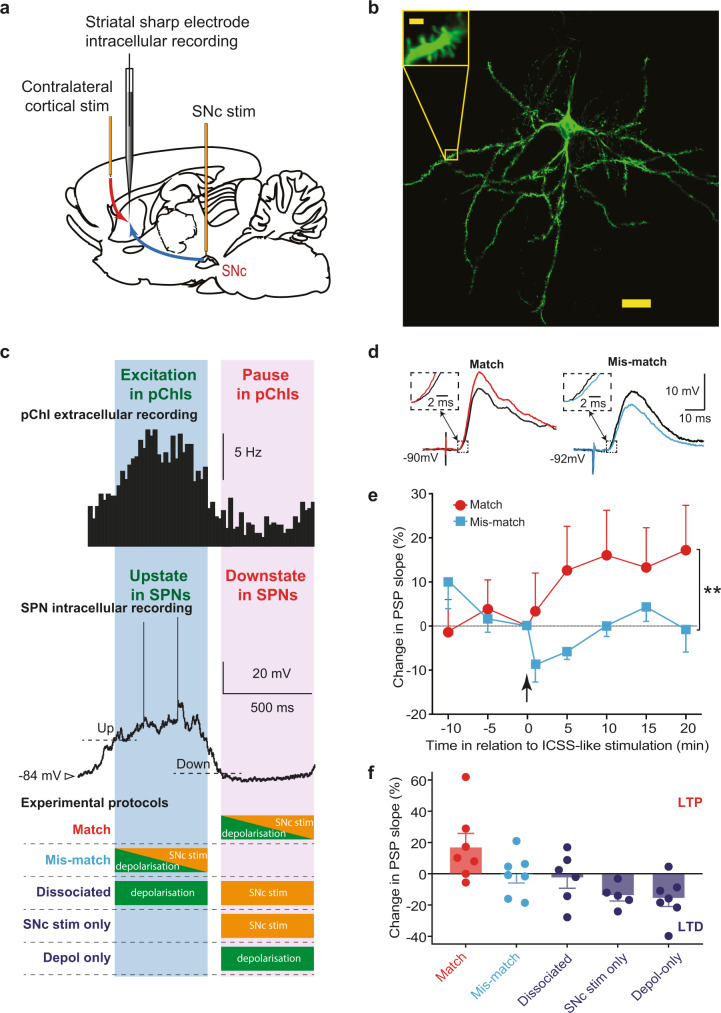
Fig. 3. Coincidence of ChI pause, dopamine activation and depolarisation potentiated corticostriatal SPN postsynaptic potentials (PSPs).
a Cortical stimulation induced PSPs in SPNs. Dopamine neurons were activated by electrical stimulation and depolarisation was induced by intracellular current injection. b A representative example from 11 labelled SPNs (Scale bar 20 µm; inset 2 µm). c Electrical stimulation of the SNc was set to match (purple shade) or mismatch (blue shade) the ChI pause, determined from the striatal iLFP. d Example corticostriatal PSPs potentiated (red) or depressed (light blue) in slope (expanded in insets) and in amplitude 20 min after baseline (black traces) when SNc stimulation matched or mismatched the ChI pause, respectively. e Group average effect on PSPs of SNc stimulation matched (N = 7) vs mismatched (N = 7); **p < 0.01 (Mean ± S.E.M.; unpaired t test at 20 min, p = 0.0025). f One-way ANOVA with Brown-Forsythe and Welch ANOVA post hoc tests to compare Match group (which induced LTP on average) to all other groups (where no change or LTD was induced): Match vs. Mismatch p = 0.008, Match vs. Dissociated (N = 6) p = 0.008, Match vs. SNc stim only (N = 5) p = 0.0005, Match vs. Depol-only (N = 7) p = 0.0010).