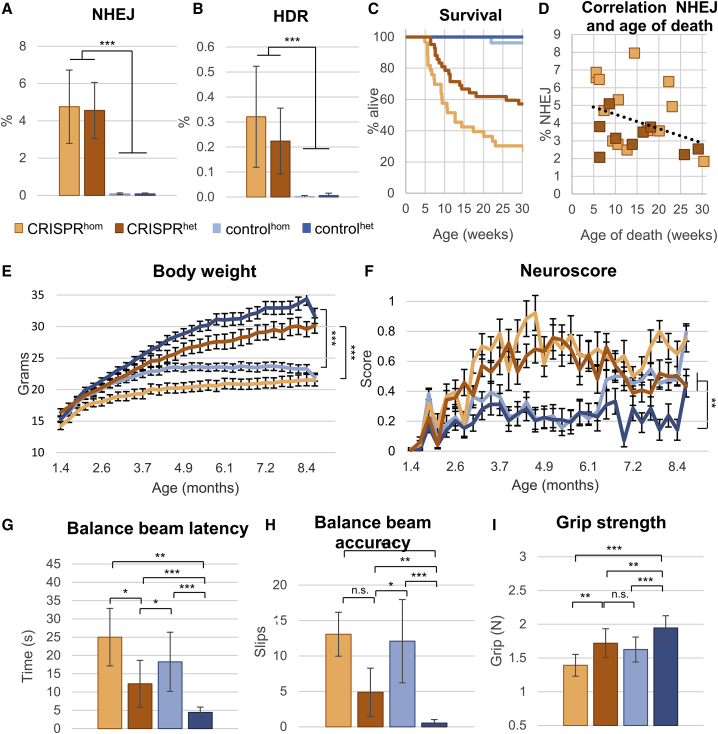
Figure 2.
The CRISPR/Cas9-induced indel to correction ratio exacerbates the VWM phenotype
(A) Next-generation sequencing (NGS) was used to assess the percentage of NHEJ edits per treatment (statistics by independent-samples t test. CRISPR n = 51, control n = 46). (B) The percentage of HDR edits per treatment, as determined by NGS (statistics by Whitney-Mann U test. CRISPR n = 51, control n = 46). (C) Survival curve of animals split into genotypes and treatment groups. (D) The correlation between age of death and percentage of NHEJ. (E) Development of body weight and (F) Neuroscore of CRISPR and control animals throughout development (CRISPR hom n = 30, het n = 42; control hom n = 40, het n = 37). (G) Speed and (H) accuracy of traversing a balance beam, as well as (I) grip strength, were assessed in 7-month-old animals (CRISPR hom n = 10, het n = 24; control hom n = 21, het n = 25). A Kruskal-Wallis test was used for (E) and (H). A Welch test with Games-Howell post hoc was used for (G). A one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc was used for (I) ∗p < .05; ∗∗p < .01; ∗∗∗p < .001. Values are represented as the mean ± SD