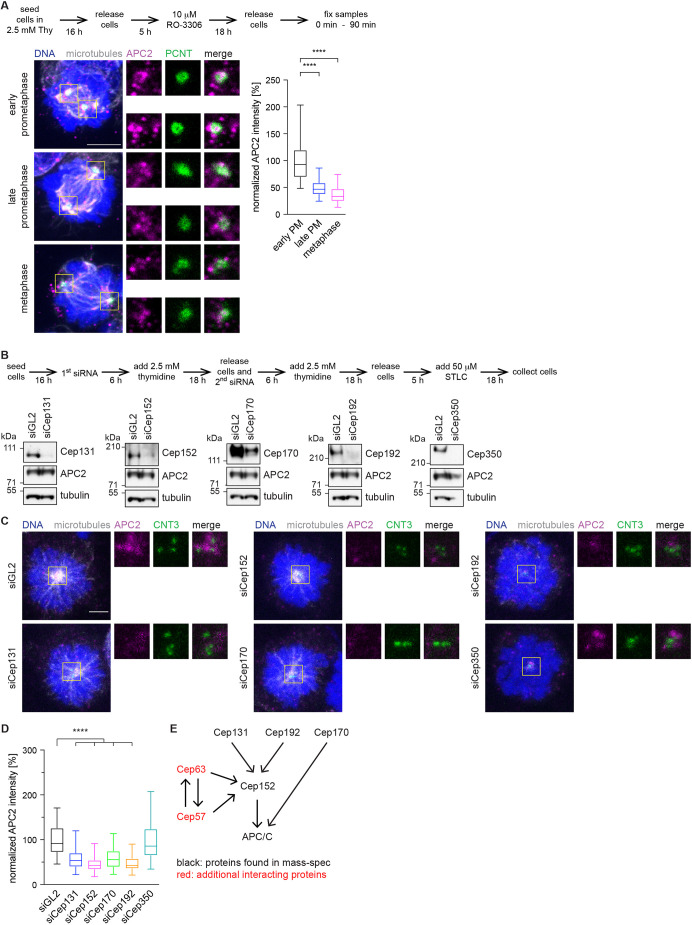
Fig. 2.
Depletion of centrosomal proteins leads to loss of the APC/C from the centrosome. (A) HEK293 cells were treated according to the timeline (top; Thy, thymidine) and stained to detect the indicated proteins. Microtubules were labelled using an α-tubulin antibody, and DNA was stained with DAPI. Boxes indicate regions shown in enlarged images. The fluorescence intensity of APC2 at the centrosome was measured as indicated in Fig. 1B and normalized against the intensity in early prometaphase (PM). N cells=77 (early PM), 130 (late PM), 73 (metaphase). (B) HEK293 cells were treated according to the timeline (top). Cells were depleted of the centrosomal proteins chosen for further analysis using siRNA (siGL2, control siRNA). Whole-cell lysates from STLC arrested, mitotic cells were immunoblotted against the indicated proteins. Tubulin serves as a loading control. Blots are representative of three experiments. (C) Cells were treated as in B and stained against the indicated proteins (CNT3, centrin-3). Microtubules were labelled using an α-tubulin antibody, and DNA was stained with DAPI. Boxes indicate regions shown in enlarged images. (D) Quantification of the APC2 intensity at the centrosome from cells shown in C. The intensity was measured as indicated in Fig. 1B and normalized against the siGL2 control. N cells=140 (siGL2), 109 (siCep131), 52 (siCep152), 86 (siCep70), 51 (siCep192), 63 (siCep350). (E) Interaction model of the different centrosomal proteins with each other and with the APC/C. Box plots show the median (line), 25–75% range (box) and 5–95% range (whiskers).****P<0.0001 (simple one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple comparison test). Scale bars: 5 µm.