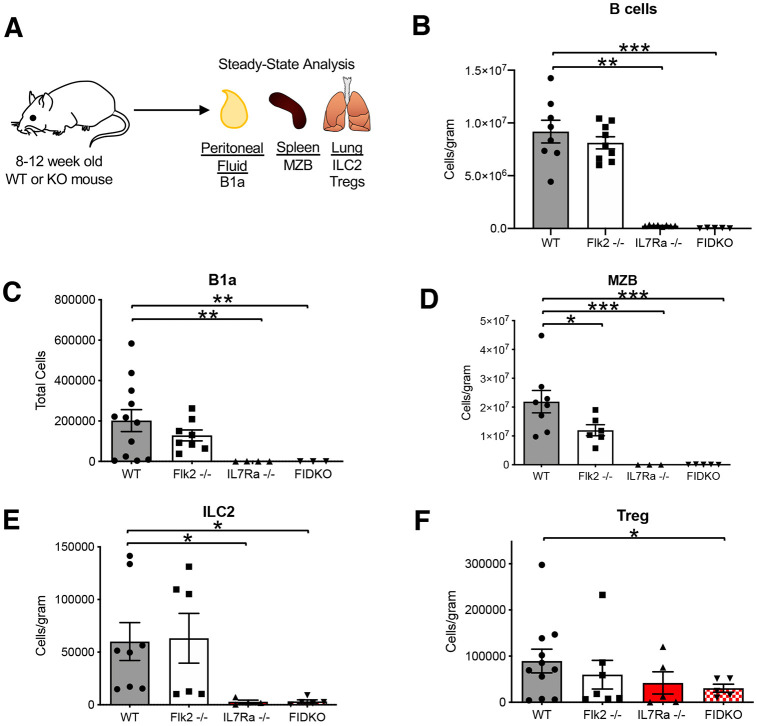
Fig. 2.
Tissue-resident lymphoid cells are severely reduced in the absence of IL7Rα, but not Flk2. (A) Schematic of experimental design: peritoneal fluid, spleen and lung from 8-12 week old WT, Flk2−/−, IL7Rα−/− and FIDKO HSCs were harvested and analyzed for cellularity of TLCs and represented in the following bar plots of WT (gray), Flk2−/− (white), IL7Rα−/− (red) and Flk2−/−/IL7Rα−/− double knockout (FIDKO; red/white). (B) Traditional B cells in the lung were significantly reduced in both IL7Rα−/− and FIDKO mice, but not in Flk2−/− mice. Quantification of B cells (Live, Ter119− Mac1− Gr1− CD19+) per gram of tissue in the lungs. (C) B1a cells in the peritoneal cavity were significantly reduced in IL7Rα−/− and FIDKO mice compared with WT. Quantification of total cell numbers in the peritoneal cavity. (D) MZBs were significantly reduced in Flk2−/−, IL7Rα−/− and FIDKO compared with WT mice. Quantification of cells/gram of tissue in the spleen. (E) ILC2s were significantly reduced in IL7Rα−/− and FIDKO compared with WT mice. Quantification of cells/gram of tissue in the lung. (F) Tregs were significantly reduced only in FIDKO compared with WT mice. Quantification of cells/gram of tissue in the lung. WT n=8 (all male), Flk2−/− n=6 (all male), IL7Rα−/− n=4 (all male), FIDKO n=5 (3 male); representing four independent experiments, mean±s.e.m. Differences were analyzed with unpaired two-tailed Student's t-test: *P<0.05, **P<0.005, ***P<0.0005.