Figure 1: Intercalated and principal cells transporters and channels within the cortical collecting duct:
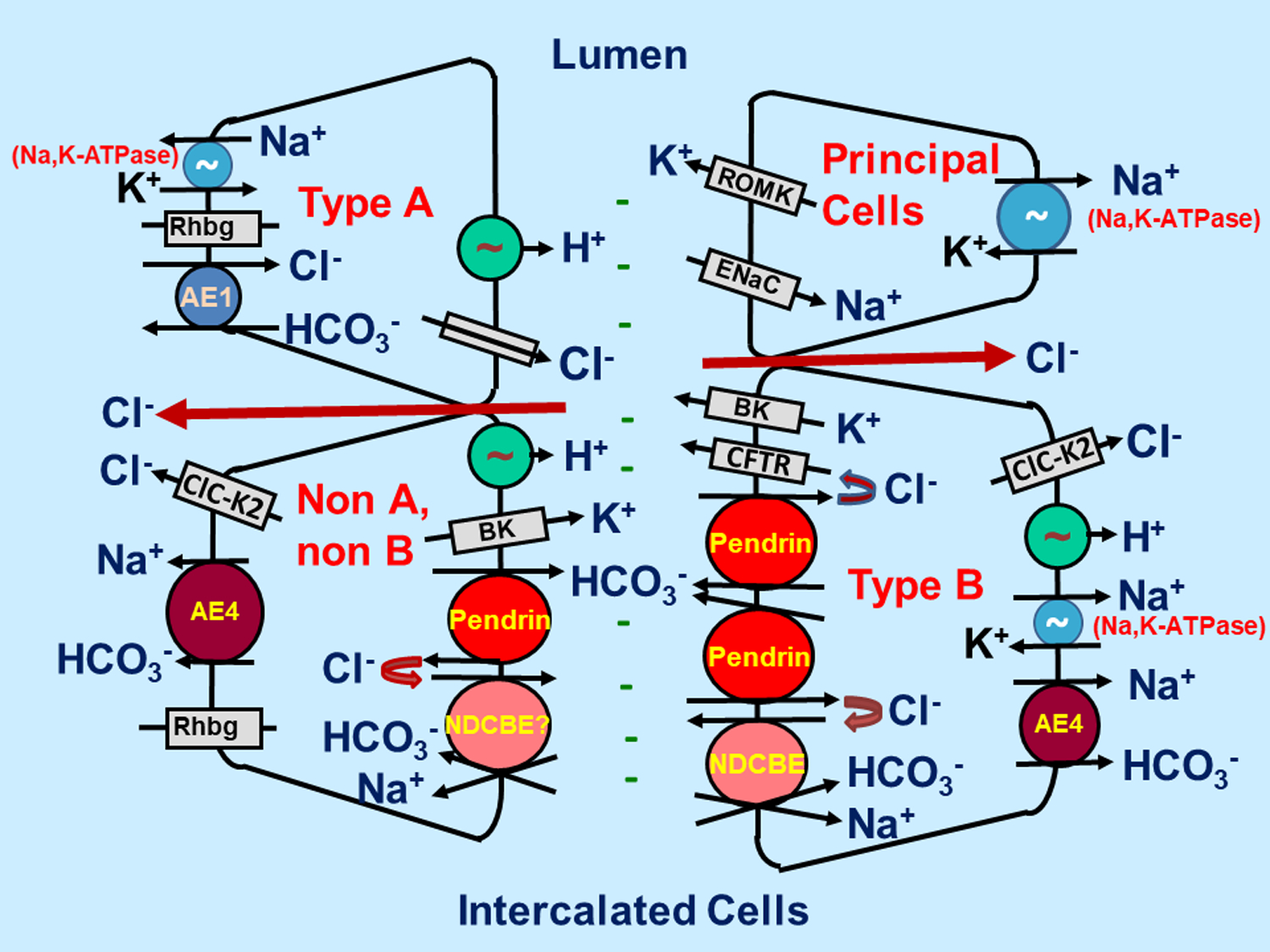
Type B ICs absorb NaCl through pendrin-mediated apical Cl− /HCO3− and the Na+-dependent Cl−/HCO3− exchanger, NDCBE, acting in tandem. Pendrin and the CFTR Cl− channel mediate HCO3− secretion, while they recycle Cl− across the apical plasma membrane. H+ and Cl− exit the cell through the basolateral plasma membrane ClC-K2 Cl− channel and the H+-ATPase, while the basolateral membrane Na+-HCO3− cotransporter, AE4, and the Na,K-ATPase mediate Na+ exit. In type A ICs the apical membrane H+-ATPase and the basolateral membrane Cl−/HCO3− exchanger, AE1, act in series to mediate H+ secretion. Principal cells absorb Na+ through the apical membrane epithelial Na+ channel, ENaC, which generates the lumen-negative transepithelial voltage, providing the driving force for K+ secretion through K+ channels such as ROMK and Maxi K+ channels.
