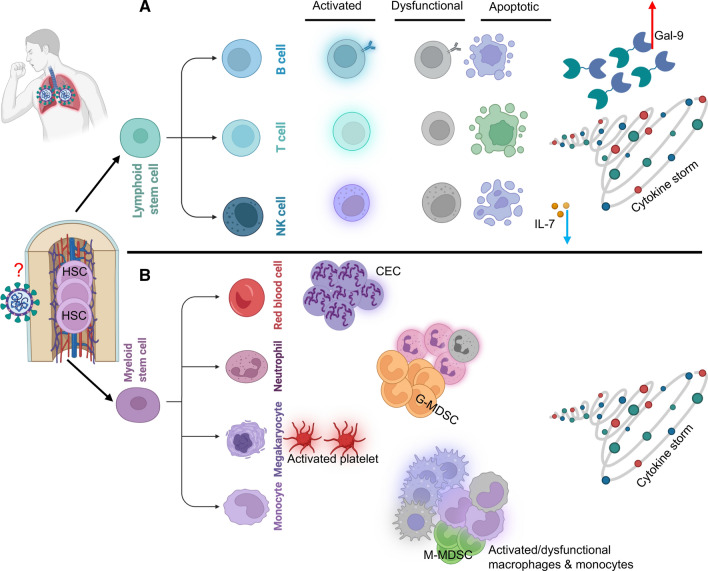
Fig. 2.
A This model illustrates the impact of COVID-19 disease on lymphoid lineage. Various studies have documented that COVID-19 disease is associated with T, B and NK cell activation. Also, some reports have shown dysfunctional/impaired lymphocytes. These highly activated lymphocytes become more prone to apoptosis as reported by the upregulation of apoptotic associated markers. Mechanistically this could be related to the direct impact of SARS-CoV-2 on HSC or associated with the general influence of the cytokine storm. Alternatively, a lower plasma IL-7 can impair lymphocyte proliferation but elevated levels of plasma Galectin (Gal-9) in COVID-19 patients may promote lymphocyte apoptosis. B In contrast, multiple reports indicated expansion of erythroid precursors/progenitors (CECs), increased number of mature and immature neutrophils (G-MDSC), activated platelets, expansion of M-MDSC, activated and/or dysfunctional macrophages and neutrophils in the blood of COVID-19 patients. In terms of mechanism(s), the direct effect of SARS-CoV-2 and cytokine storm on HSC have been proposed