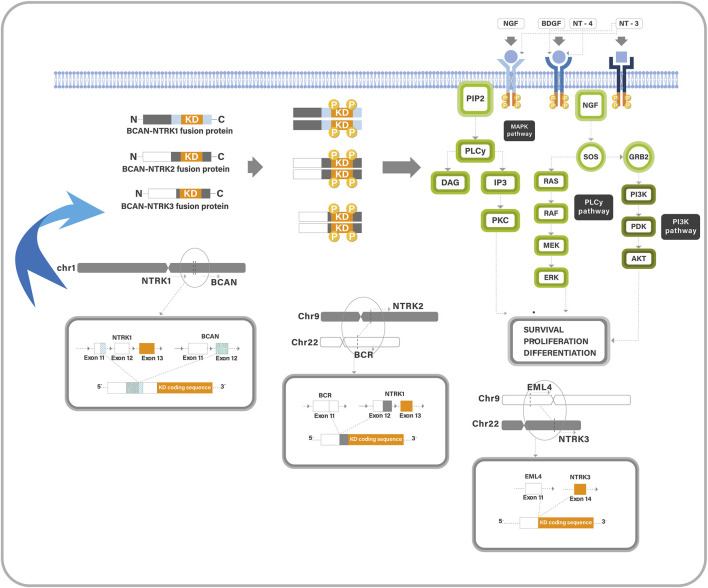
FIGURE 1.
A diagram describes the Trk pathway and the oncogenic mechanism of NTRK-fusions. Trk proteins contain an intracellular TK domain which promotes cell proliferation through MAPK/ERK, PLCg/PKC, and PI3K/AKT pathways. Trk-fusion proteins have a complete TK domain, and the partner gene is expressed in a homodimer, which induces ligand-independent activation of the TK domain. It also activates the cancer-associated pathways.