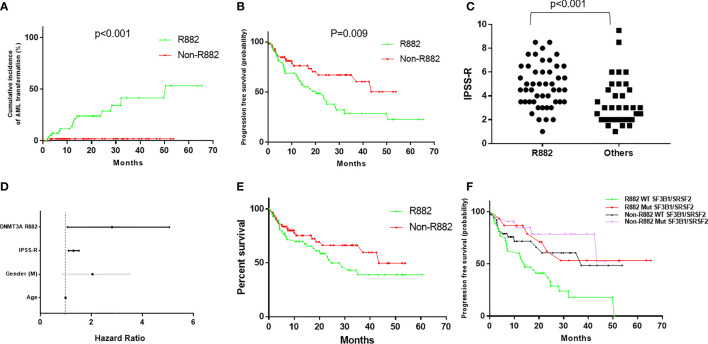
Figure 4.
DNMT3A R882 mutations confer increased risk of AML transformation and worse progression free survival in MDS, which are masked by the coexisting SF3B1 or SRSF2 mutations. (A) Cumulative incidence of AML transformation in DNMT3A (R882 vs. Non-R882) mutant MDS. (B) Progression free survival analysis in patients with DNMT3A (R882 vs. Non-R882) mutant myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). (C) The distribution of IPSS-R scores in the R882 group and the other group. (D) Cox proportional hazards model analysis of risk factors for worse progression free survival. Statistically significant factors are highlighted with black lines. (E) Overall survival analysis in patients with DNMT3A (R882 vs. Non-R882) mutant myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). (F) Progression free survival analysis in DNMT3A (R882 vs. Non-R882) mutant MDS with mutant and wildtype SF3B1/SRSF2.