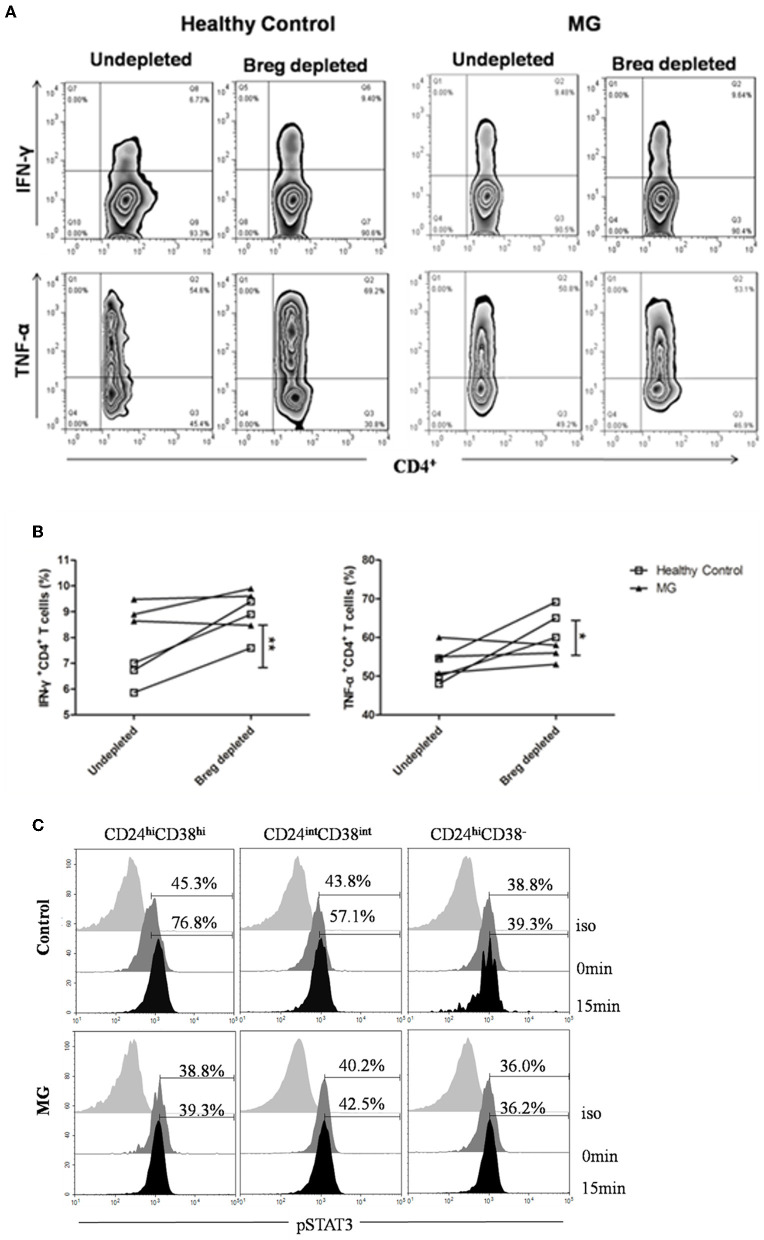
Figure 5.
CD19+CD24hiCD38hi B cells from MG patients fail to suppress IFN-γ+ and TNF-α+CD4+ T cell differentiation. B cells isolated from patients with MG or healthy controls were stained with CD19, CD24, and CD38 and gated, as shown in Figure 2A. CD19+CD38hiCD24hi B cells were depleted, and the depleted B cells and undepleted B cells were both collected using flow cytometry sorting. CD4+ T cells were collected by magnetic-bead purification, and then, B cells and CD4+ T cells were cocultured for 72 h with 0.5 mg/ml plate-bound CD3 mAb. PMA+iono was added for the last 6 h of culture. Depleted and undepleted B cells were surface stained with CD4 and CD19 mAbs, permeabilized, and stained with TNF-α or IFN-γ mAbs. (A) Representative flow cytometry plots for IFN-γ+ and TNF-α+CD4+ T cells in MG patients and healthy controls according to whether CD19+CD38hiCD24hi B cells were depleted or undepleted. (B) Graphs showing the differences in the frequency of IFN-γ+CD4+ and TNF-α+CD4+ T cells between depleted and undepleted B cells from the same individual. Healthy individuals are indicated by white squares, and MGs are indicated by black triangles. The results from three healthy individuals and three MG patients are shown. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. (C) Representative histograms of pSTAT-3 expression by CD19+CD24hiCD38hi, CD19+CD24intCD38int, and CD19+CD24+CD38− B cells at 0 and 15 min post-stimulation with CD40 mAb for one MG patient and one healthy control.