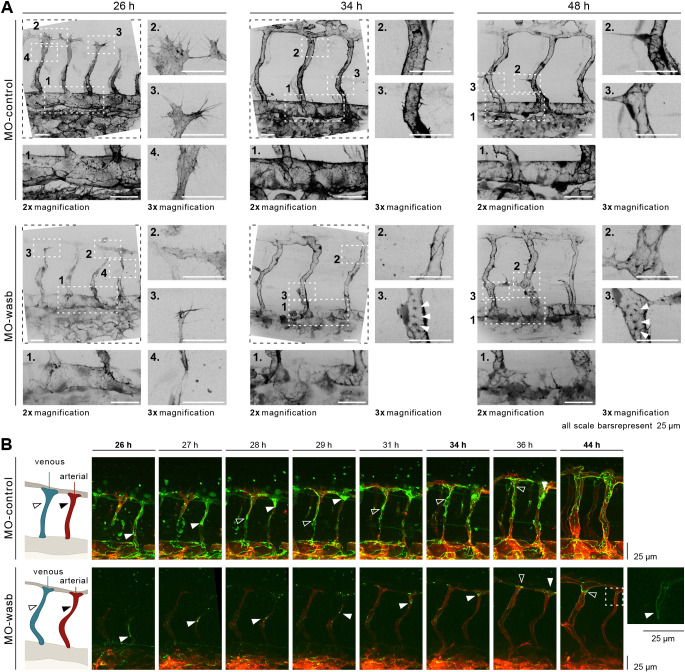
Fig. 5.
Wasb is required for F-actin regulation and junctional Pecam1 localization. (A) Upper panel: trunk vasculature of Tg[fliep:lifeactGFP] MO-control. F-actin is mostly prominent at 26 hpf in filopodia (inset 3), cell-cell contacts of anastomosis (inset 2), cell cortex and stress fibres (inset 4). In the DA, F-actin accumulates at cell junctions (inset 1). At 34 hpf and later at 48 hpf F-actin is enriched at junctions of ISV (insets 2 and 3) and DA (insets 1). Lower panel: trunk vasculature of Tg[fliep:lifeactGFP] MO-wasb. F-actin is decreased during anastomosis (inset 3) with heterogeneous accumulation at the cortex and loss of stress fibres (inset 4). Filopodia still show F-actin accumulation (inset 2). In the DA junctional F-actin is lost (inset 1). At 34 hpf and later at 48 hpf junctional accumulation is heterogenous (insets 2) and in the form of puncta (insets 3). In the DA F-actin has heterogeneous accumulation (insets 1). (B) MO-control: Pecam1 (green) junctional localization in remodelling vessels labels migratory cells. White arrowhead labels migratory stalk EC in aISV. Dorsal movement from 26 to 29 h. Diffuse Pecam1 localization at 34 hpf. Ventral movement at 36 hpf. Black arrowhead labels migratory stalk EC in vISV with dorsal movement from 28 to 36 hpf. MO-wasb: Pecam1 is lost or reduced in EC junctions. White arrowhead labels migratory stalk EC in aISVs with dorsal movement from 26 to 36 hpf. Inset (right) labels second stalk cell with ventral-to-dorsal orientation. Black arrowhead labels migratory EC entering vISV from 36 to 44 h. Red labels ECs membrane.