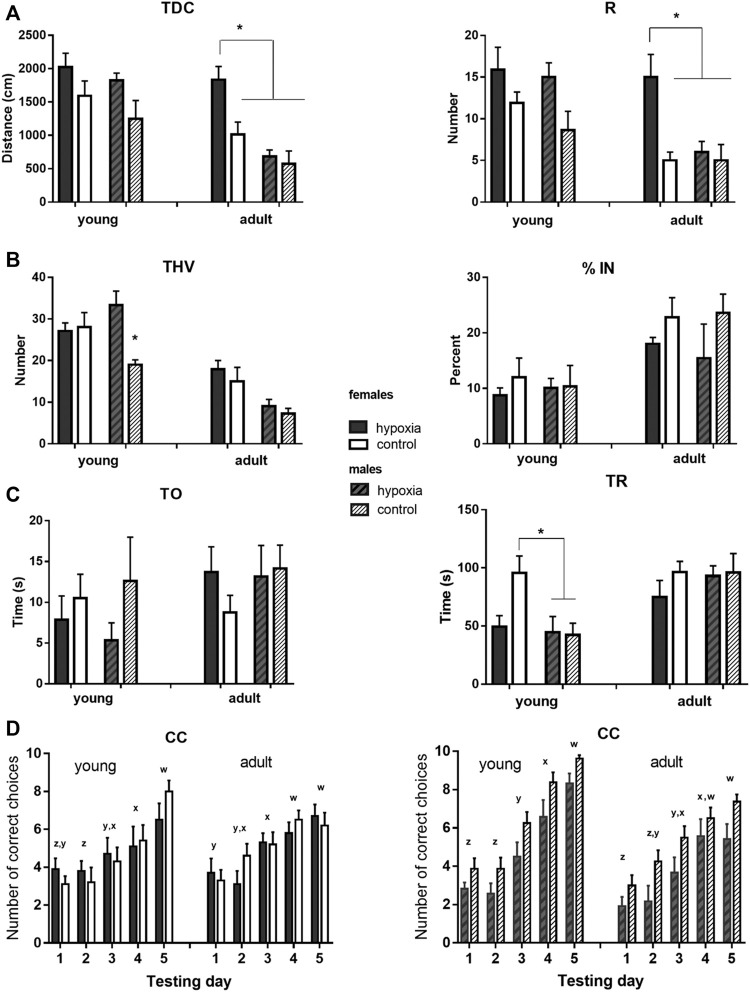
FIGURE 4.
Results of the behavioral testing in young and mature animals display altered behavior and cognition in juvenile and adult rats. The rats were exposed to a battery of behavioral tests at juvenile (adolescent) (P33-P41) and adult (P83-P91) ages, to examine whether any behavioral and cognitive differences were still present or had newly appeared in adulthood. (A) Locomotor activity was measured as the total distance covered (TDC) and the number of rearing times (R) in an open field. Two-way ANOVA revealed: for TDC, a significant influence of hypoxia in juveniles and of hypoxia, sex, and hypoxia-sex interaction in the adults; for R, there was a significant influence of hypoxia in juveniles and a significant influence of hypoxia and sex, with the indicative influence of hypoxia-sex interaction in the adults. (B) Exploratory behavior was measured as the total number of visited holes (THV), and anxiety-like behavior was measured as the percentage of visited inner holes (% IN) in a hole-board. Two-way ANOVA revealed: for THV, a significant influence of hypoxia and hypoxia-sex interaction in juveniles and a significant impact of sex in adults; for % IN, no significant influences. (C) Social behavior was measured as time spent exploring an object (TO) and time spent exploring a rat (TR) in a social choice apparatus. Two-way ANOVA revealed for TO, no significant influences; for TR, a significant influence of sex, and hypoxia x sex interaction, only in juveniles. (D) Learning abilities were measured in a T-maze separately for males and females, and as the number of correct choices (CC) in sessions of ten trials during five consecutive days. Repeated measure two-way ANOVA revealed: for males, a significant influence of hypoxia and time, in juveniles, and an indicative influence of hypoxia and a significant effect of time, in adults; for females, the analysis showed a significant influence of time, in both juveniles and adults. Results are shown as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM); Tukey’s honestly significance post-hoc test was performed after establishing a significant/indicative hypoxia-sex interaction influence and values that significantly differ are marked with an *(A–C). Letters x-z are indicators of significant differences (different letters) or the lack of significant difference (same letters) in the mean number of correct choices among different testing days as revealed by Tukey’s honestly significance post-hoc test (D).