Fig. 8.
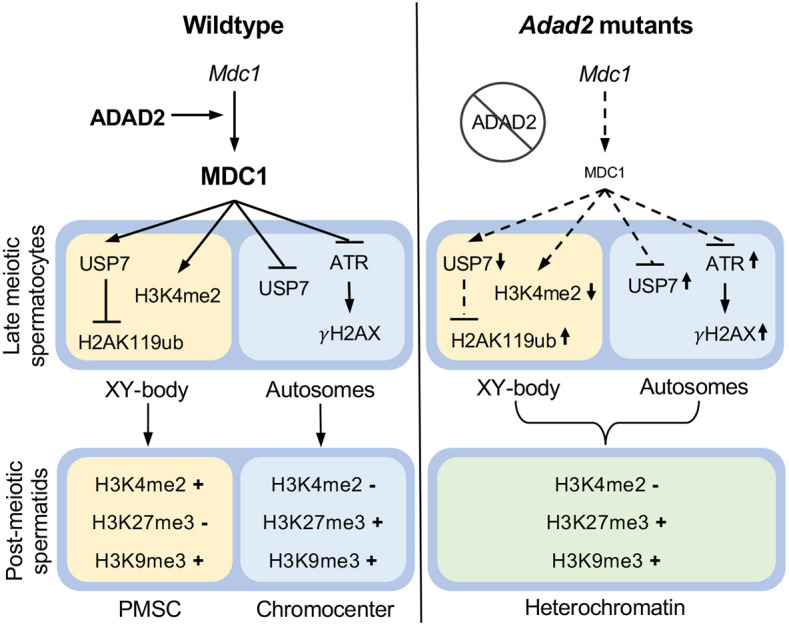
Summary of ADAD2 action and drivers of the Adad2 mutant phenotype. In wild-type germ cells, ADAD2 facilitates translation of Mdc1 late in meiosis, thus ensuring the correct epigenetic state of the XY body and autosomes, and resulting in two unique heterochromatin domains (PMSC and the chromocenter) in the subsequent post-meiotic germ cells. In the absence of ADAD2, MDC1 is low late in meiosis, leading to abnormal XY-body and autosome epigenetic signatures in late meiotic spermatocytes. In mutant post-meiotic spermatids, improperly marked chromatin domains result in the loss of distinct chromatin compartments.
