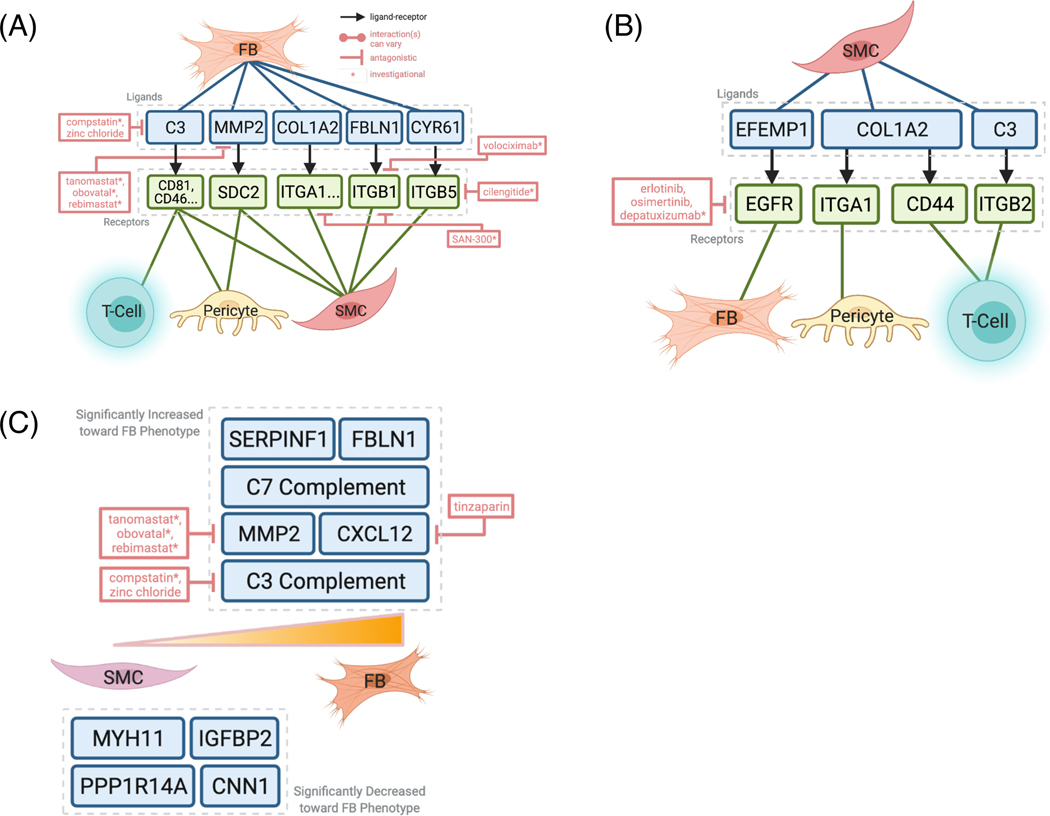
Figure 3.
Integrative analysis with drug-gene interaction database DGIdb 3.0 reveals potential pharmacological inhibition of SMC and FB signaling and dedifferentiation.
(A) ‘scTalk’ shows that FBs signals to T-cells, pericytes, and SMCs through pro-inflammatory molecules like C3, which can be targeted by the experimental drug compstatin. (B) SMCs interact with FBs through at least four pairs of experimentally verified interactions. Of these, complement and EFEMP1-EGFR signaling is the most druggable as revealed by DGIdb 3.0. (C) Druggable genome analysis revealed agents that can target genes along the SMC-FB de-differentiation trajectory, such as C3, C-XC Motif Chemokine Ligand 12 (CXCL12), and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP2).