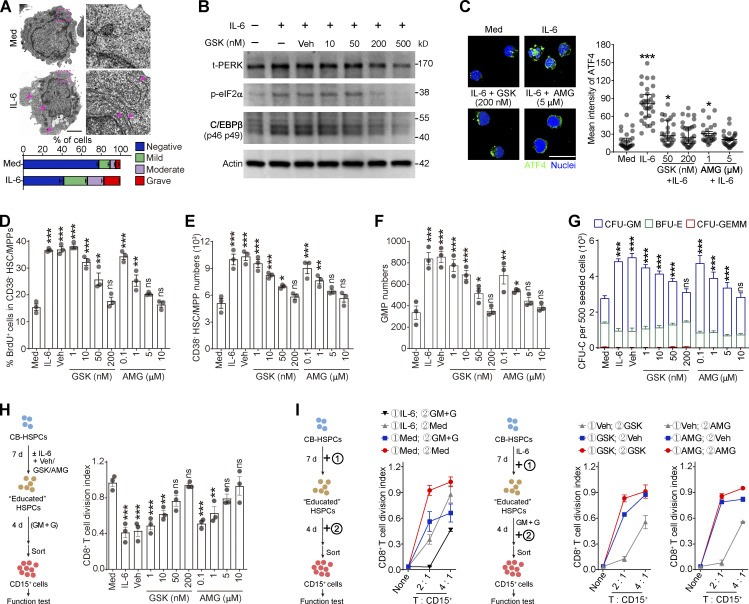
Figure 7.
Activation of PERK–ATF4–C/EBPβ signaling is essential for human HSPC differentiation into MDSCs. (A) Representative microphotographs of CB-HSPC morphology. Arrows denote dilated ER. Scale bar, 2 μm; Med, SFEM supplemented with SCF, TPO, and Flt3L. (B) IB analysis of total PERK (t-PERK), C/EBPβ, and p-eIF2α levels in CB-HSPCs cultured under the indicated conditions. (C) Expression and distribution of ATF4 in cultured human HSPCs. Scale bar, 25 μm. (D) Effects of PERK inhibitors on CD34+CD38− HSC/MPP proliferation. (E and F) Numbers of HSCs/MPPs (E) and GMPs (F) after 72 h of culture of 500 lin−CD34+CD38− HSCs/MPPs. (G) CFU-C activity in the cultured HSPCs on day 7. (H and I) Suppressive activity of CD15+ myeloid cells generated from CD34+ HSPCs under the indicated conditions. GM, GM-CSF; G, G-CSF. Error bars indicate means ± SEM (A and D–I) or median and IQR (C). Statistics: Kruskal–Wallis test (C); one-way (D–F and H) or two-way (G) ANOVA corrected by Dunnett’s test. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. Data are from three independent experiments (n = 3 samples per group) or are representative of three independent experiments (B and C). Source data are available for this figure: SourceDataF7.