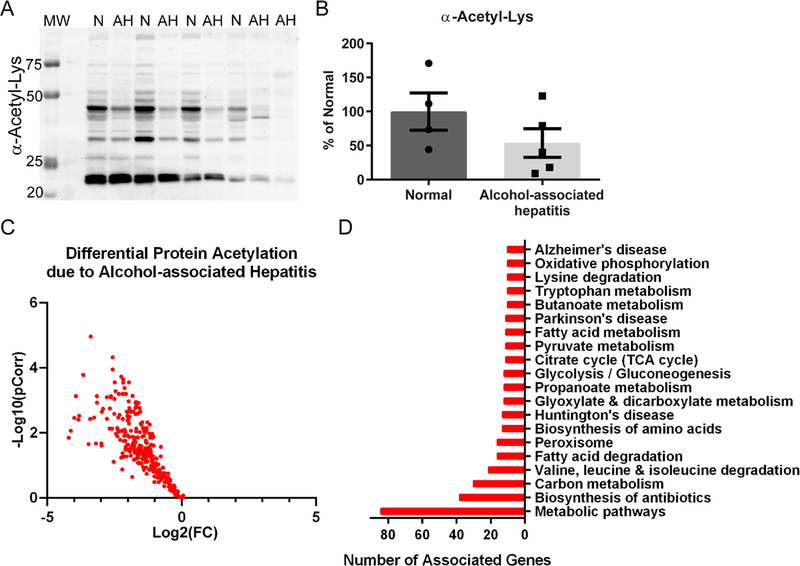
Figure 4. Acetylomic analysis of hepatic tissue from normal and alcohol-associated hepatitis explants.
(A) Western blotting for global protein acetylation on cytoplasmic-enriched liver lysates revealed a consistent decrease in AH tissue. Normal, n=4; AH, n=5. N: normal; MW: molecular weight ladder (B) Quantitation demonstrated a trend of decreased acetyl-Lys in AH samples. (C) Protein acetylation was found to be significantly decreased by quantitative mass spectrometry in AH versus normal explant tissue, as illustrated in the volcano plot. Normal, n=5; AH, n=4. (D) The bar chart highlights the top 20 KEGG pathways associated with the observed AH-induced decrease in protein acetylation. Overall, analysis of AH explant tissue not enriched for chromatin revealed a decrease in protein acetylation across metabolic, antioxidant, and disease-associated pathways.